Chapter 10 Small-Caliber Endoscopy
![]() Video related to this chapter’s topics: Small-Caliber Endoscopy
Video related to this chapter’s topics: Small-Caliber Endoscopy
Introduction
Small-caliber endoscopy has other practical uses. Patients who may be predictably intolerant of endoscopy with sedation, such as young patients, are potential candidates for this option. Small-caliber endoscopy offers a dramatically reduced procedure stress for patients who have fragile cardiopulmonary disease. The small-caliber endoscope provides an effective and well-tolerated option for the placement of transnasal feeding tubes and the placement of jejunal extensions via an existing percutaneous feeding gastroscopy site.1–3 Patients with high-grade esophageal strictures with existing percutaneous feeding gastrostomy may have primary or rendezvous attempts at dilation with placement of guidewires using a small-caliber endoscope via the gastrostomy site.4,5
Small-Caliber Endoscopy Insertion Techniques
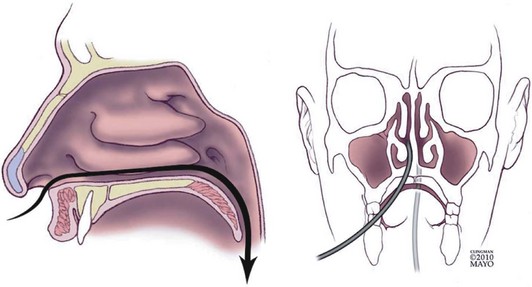
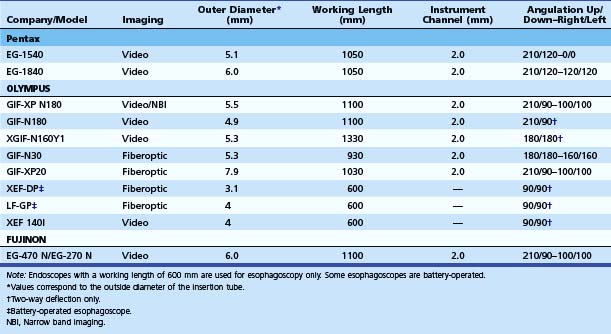
Small-caliber upper endoscopy can be performed either transnasally or perorally (Fig. 10.1). Transnasal endoscopy is feasible with endoscopes measuring 6 mm or less in outside diameter. Table 10.1 summarizes specifications of small-caliber endoscopes used in the reviewed studies and other endoscopes that are commercially available. Both videoesophagogastroduodenoscopes and esophagoscopes are currently available. Videoesophagogastroduodenoscopes have a working length of 1030 to 1330 mm, and esophagoscopes have a working length of only 600 mm. The outer diameter of videoesophagogastroduodenoscopes is between 5.1 mm and 6 mm. Esophagoscopes have an outside diameter between 3.1 mm and 4 mm. The relative outside diameters of small-caliber pediatric and conventional esophagogastroduodenoscopes are shown in Fig. 10.2A. Some esophagogastroduodenoscopes allow right and left and up and down angulation, whereas others provide only up and down angulation (Fig. 10.2B).
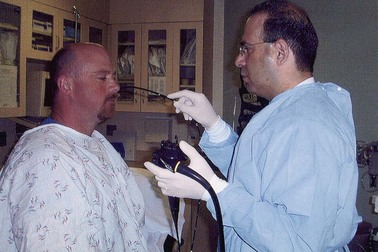
The procedure can be performed either in the standard left lateral decubitus position for conventional endoscopy or in the upright position (Fig. 10.3). Whether the upright position decreases the aspiration risk is unknown. The transnasal procedure should be performed with minimal air insufflation. The endoscope should be inserted slowly and gently, keeping the insertion tube of the endoscope straight such that it passes along the floor and septum of the nasal cavity and it does not migrate upward and laterally into turbinates interrupting passage, causing pain, and inducing bleeding. Slow progressive insertion with flexion of the endoscope tip over the base of the tongue is recommended for unsedated peroral examinations. Vigorous movements of the endoscope cause greater nasal discomfort with the transnasal route and more gagging with the peroral approach. During the procedure, conversing with the patient and pointing out findings on the video monitor reassure patients and may improve tolerability and reduce discomfort.
Unsedated Small-Caliber Upper Endoscopy
Technical Feasibility of Unsedated Small-Caliber Endoscopy
Feasibility of unsedated small-caliber endoscopy is mainly a subjective measure defined by the endoscopist. It can be affected by many factors, including the diameter of the small-caliber endoscope, endoscope maneuverability, image quality, patient tolerability, and the skills of the endoscopist. Feasibility of unsedated endoscopy is particularly linked to tolerance, which is discussed in the next section. In the crudest sense, technical feasibility represents the successful completion of the intended procedure by intubating the duodenum if an EGD is being performed or intubating the stomach if esophagoscopy is being done. Several investigators have reported the feasibility of transoral or transnasal unsedated EGD.6–18 Most of these studies have not been prospective randomized controlled trials. The patient populations have been either small in size or not representative of the general U.S. population. Studies addressing the feasibility of EGD that warrant attention are described next.
Wilkins and coworkers6 randomly assigned 72 patients to undergo either unsedated small-caliber EGD or sedated conventional EGD. Despite a highly selected and motivated U.S. Air Force community population, only 29 of the 33 patients (88%) had a complete unsedated small-caliber EGD. In another controlled study, Mulcahy and coworkers7 compared the feasibility of unsedated small-caliber EGD with unsedated conventional EGD in 322 patients. EGD was completed in 160 of the 163 patients (98%) undergoing unsedated EGD with a 6-mm gastroscope compared with 145 of the 159 patients (91%) undergoing unsedated EGD with a 9.8-mm gastroscope. These investigators subsequently reported 39 (8%) failures in a prospective study of 508 patients undergoing routine unsedated gastroscopy.8 Failure was associated with larger scope diameter (>9 mm), higher preprocedure anxiety, and younger age.
Ristikankare and colleagues9 randomly assigned 180 patients undergoing EGD to receive intravenous (IV) midazolam, IV saline, or no IV access. Although the procedure was perceived “less difficult” in the IV midazolam group compared with the IV saline group, the difference was not statistically significant. The power to detect differences between the three groups was not determined in this study. The small patient population and the lack of validated criteria to assess the difficulty of an EGD limit the utility of the evidence.
The feasibility of unsedated small-caliber EGD was also assessed as part of the multiphase Mayo Clinic Rochester study of a select group of highly motivated patients and volunteers.10 The second portion of the duodenum was reached in 20 sedated and 20 unsedated volunteers in this prospective, nonrandomized study. Among the patients, 50 subjects successfully underwent sedated small-caliber EGD followed by sedated conventional EGD, and 38 of 40 patients underwent successful unsedated small-caliber EGD followed by sedated conventional EGD. Overall, the technical feasibility was not significantly affected by sedation in this study. A type II error (failure to detect a significant difference when there is a difference) cannot be ruled out, however, because the sample size to detect a significant difference was not calculated.
Investigators have also studied the feasibility of unsedated transnasal small-caliber EGD. Saeian and coworkers11 showed that unsedated transnasal esophagoscopy with a 5.3-mm gastroscope was feasible in 15 cirrhotic patients. The study was uncontrolled, and the population was very small. Zaman and colleagues13 compared peroral and transnasal approaches for EGD with the same small-caliber instrument using a prospective randomized crossover study design. Of 105 patients, 60 (57%) agreed to undergo unsedated small-caliber EGD. Peroral unsedated EGD was feasible in 34 of 35 (97%) patients, including 4 who failed transnasal EGD and were crossed over. Unsedated transnasal EGD was feasible in only 25 of 29 (86%) patients. The statistics were not reported, and a sample size based on a study hypothesis was also not calculated before study initiation.
Campo and coworkers14 randomly assigned 181 Spanish patients to undergo transnasal small-caliber EGD or peroral conventional EGD. Insertion failed in six (3.3%) patients; four had been randomly assigned to the transnasal route and two to the peroral route. In a prospective randomized trial in Australia, Craig and colleagues17 compared the feasibility of unsedated transnasal with unsedated peroral small-caliber EGD. A complete examination was feasible in 74 of the 84 (88%) transnasal and 85 of the 86 (99%) transoral procedures (P = .004).
Dumortier and coworkers18 reported that unsedated transnasal EGD was feasible in 1033 of 1100 (94%) patients studied prospectively at three French medical centers. Failures were mainly due to the inability to insert the small-caliber endoscope (62.7%). Other reasons for failure included patient refusal and nasal pain. In their prior study published in 1999, the same investigators showed that unsedated transnasal EGD was feasible in 82% of the study population and was associated with less nausea and choking.19 The feasibility of transnasal small-caliber EGD was initially assessed in 100 patients in this two-phase study; 150 patients were then randomly assigned to undergo peroral conventional EGD with a 9.8-mm videoendoscope, peroral small-caliber EGD with a 6-mm videoendoscope, or transnasal small-caliber EGD with a 6-mm videoendoscope.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree