■ Computed tomography (CT) scan—A triphasic CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with fine cuts through the pancreas is the mainstay of imaging for pancreatic pathology. CT allows for characterization of the pancreatic mass, identifies involvement of the mesenteric vessels, and evaluates for metastatic disease, particularly in the liver or lungs.
■ Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)—This diagnostic modality, although not routinely performed at all institutions, should be considered standard of care in most cases. EUS allows for visualization and biopsy of the mass, particularly if a tissue diagnosis is required for treatment with neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy. Mesenteric vessel involvement can be evaluated. Additionally, suspicious lymph nodes can be identified and biopsied, which helps to accurately stage the patient.
■ Staging laparoscopy—The role of staging laparoscopy in the management of pancreatic cancer remains controversial and is not routinely performed at most institutions.3 For patients with large tumors, equivocal CT findings, or highly elevated carbohydrate antigen (CA 19-9), staging laparoscopy can be considered.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Preoperative Planning
■ Determining resectability based on high-quality diagnostic and imaging modalities is the key step in preoperative planning, particularly because the use of the robotic technique precludes the ability of the surgeon to palpate the tumor and readily identify vascular involvement intraoperatively.
■ Four units of crossmatched packed red blood cells should be prepared and available.
■ Preoperative antibiotics should be administered.
Positioning
■ The general setup for the robotic operating room is depicted in FIG 2.
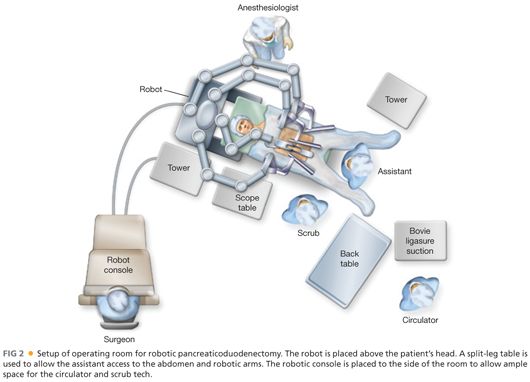
■ The patient is positioned supine on a split-leg table, which allows space for the assistant surgeon to have access to the abdomen. The right arm is tucked with protective foam padding.
■ Prior to the start of the procedure, central and arterial lines are inserted in addition to a nasogastric tube and Foley catheter. A convective warming blanket is used on the upper body.
TECHNIQUES
PORT PLACEMENT
■ Seven ports are used for robotic assistance during pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ports include a 10-mm camera port, three robotic arm ports, two assistant ports, and a 5-mm liver retractor port. Our port location and configuration is displayed in FIG 3.
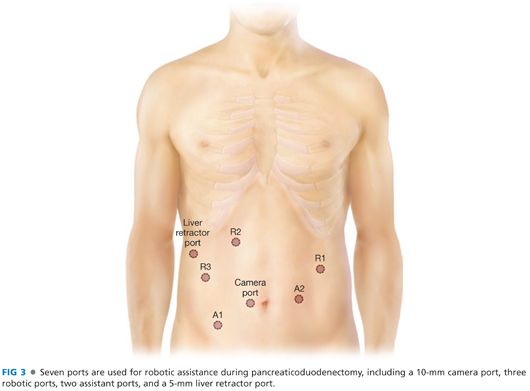
■ Access to the abdomen is obtained using a 5-mm optical separator port inserted to the left of the umbilicus in the midclavicular line. This port is eventually upsized to 8 mm and serves as a robotic arm.
■ A 4- to 5-cm incision to extract the specimen is placed in the left midclavicular line.
MOBILIZATION OF THE RIGHT COLON AND DUODENUM
■ Standard laparoscopic instruments including an atraumatic grasper and bipolar electrocautery are used to fully mobilize the right colon.
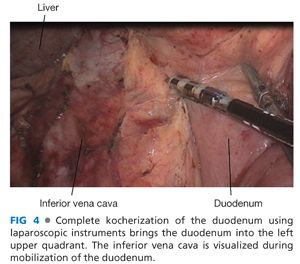
■ The duodenum is kocherized with mobilization of the third and fourth portion until the jejunum reaches into the right upper quadrant and the SMV is exposed at the root of the small bowel mesentery (FIG 4).
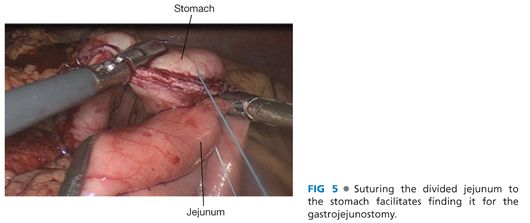
■ The jejunum is transected 10 cm distal to the ligament of Treitz using a linear stapler. The proximal jejunum is passed back under the superior mesenteric vessels. The distal jejunum is then marked with a suture at aprproximately 50 cm and secured to the stomach in an antecolic fashion, ensuring it is easily identified for reconstruction of the gastrojejunostomy (FIG 5).
MOBILIZATION AND DIVISION OF THE STOMACH
■ Continuing laparoscopically, the lesser sac is entered by division of the gastrocolic omentum. The posterior stomach is freed from the anterior pancreas.
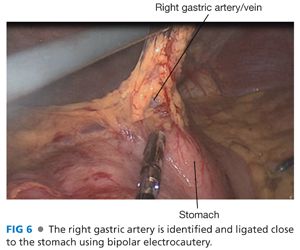
■ The right gastric and right gastroepiploic arteries are ligated close to the stomach with a bipolar electrocautery device and clips (FIG 6).
■
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








