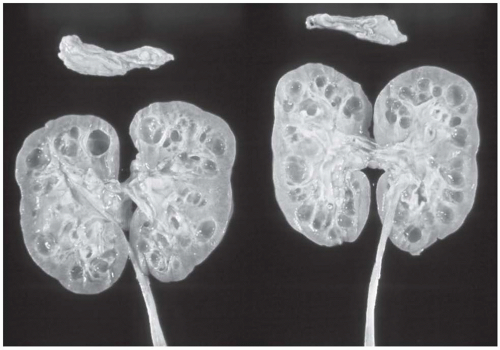
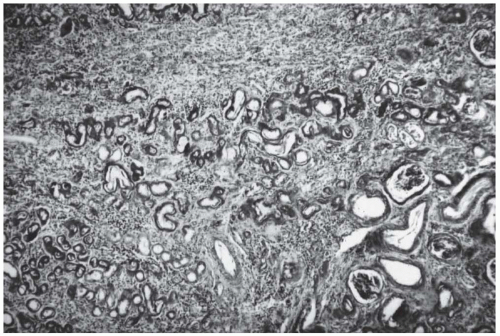
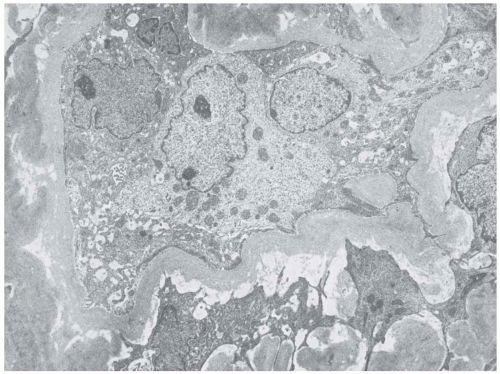
have been destroyed by the tubular alterations. An escape of Tamm-Horsfall (uromodulin) protein from damaged collecting tubules into the interstitium has been demonstrated in about 50% of patients with NPHP-MCKD as a periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive material and by specific immunofluorescence staining with an anti-THP antibody.8 Immunofluorescence does not otherwise contribute to the diagnosis of NPHP-MCKD.
TABLE 15.1 Shared and Distinguishing Features Among Diseases of the NPHP-MCKD Complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
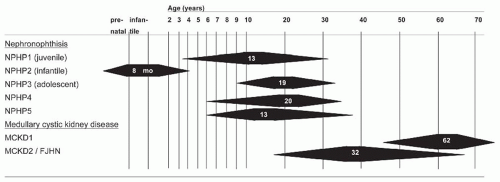
For the recessive forms the term nephronophthisis (NPHP) is used, whereas the designation medullary cystic kidney disease (MCKD) denotes the dominant variants of the complex (Table 15.1B[i]).10,11
of hyperuricemia and gout in MCKD123 and MCKD2.22 MCKD2 patients with UMOD mutations also may exhibit defects in urine concentrating ability.24 Recently, an extensive study on genotype-phenotype correlations in mutation of NPHP genes has been published.25 NPHP1 can occur in combination with ocular motor apraxia Cogan type,26,27 with retinitis pigmentosa in Senior-Løken syndrome (SLSN),20 with liver fibrosis28 with cone-shaped epiphyses in Mainzer-Saldino syndrome,29 and with coloboma of the optic nerve and cerebellar vermis aplasia in Joubert syndrome type B (JBTSB) (Tables 15.1B[iii] and 15.2).30 Infantile NPHP (type 2) can be associated with situs inversus31 and one case report describes a patient with a nonsense inversin mutation with retinitis pigmentosa.32 NPHP4 patients may have retinitis pigmentosa (SLSN) and Cogan syndrome.33 NPHP5 patients display early onset retinitis pigmentosa (SLSN) in all known cases.20 NPHP6 and NPHP8 patients have SLSN, Joubert syndrome, or Meckel-Gruber syndrome (MKS).25,34,35 NPHP9 is associated with SLSN.36 NPHP10 patients display SLSN and Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS)-like phenotypes,37 whereas patients with NPHP11 show JBTS, MKS, and liver fibrosis.38,39 NPHP12 patients exhibit Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy.40
Inversin localizes to primary cilia, mitotic spindles, and centrosomes74 and is intimately associated with the microtubule cytoskeleton.75 INVS/NPHP2 mutations remain a rare cause of NPHP, accounting for <1% of cases.
TABLE 15.2 Disease Variants, Gene Loci, and Extrarenal Involvement in the NPHP-MCKD Complex of Diseases | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree