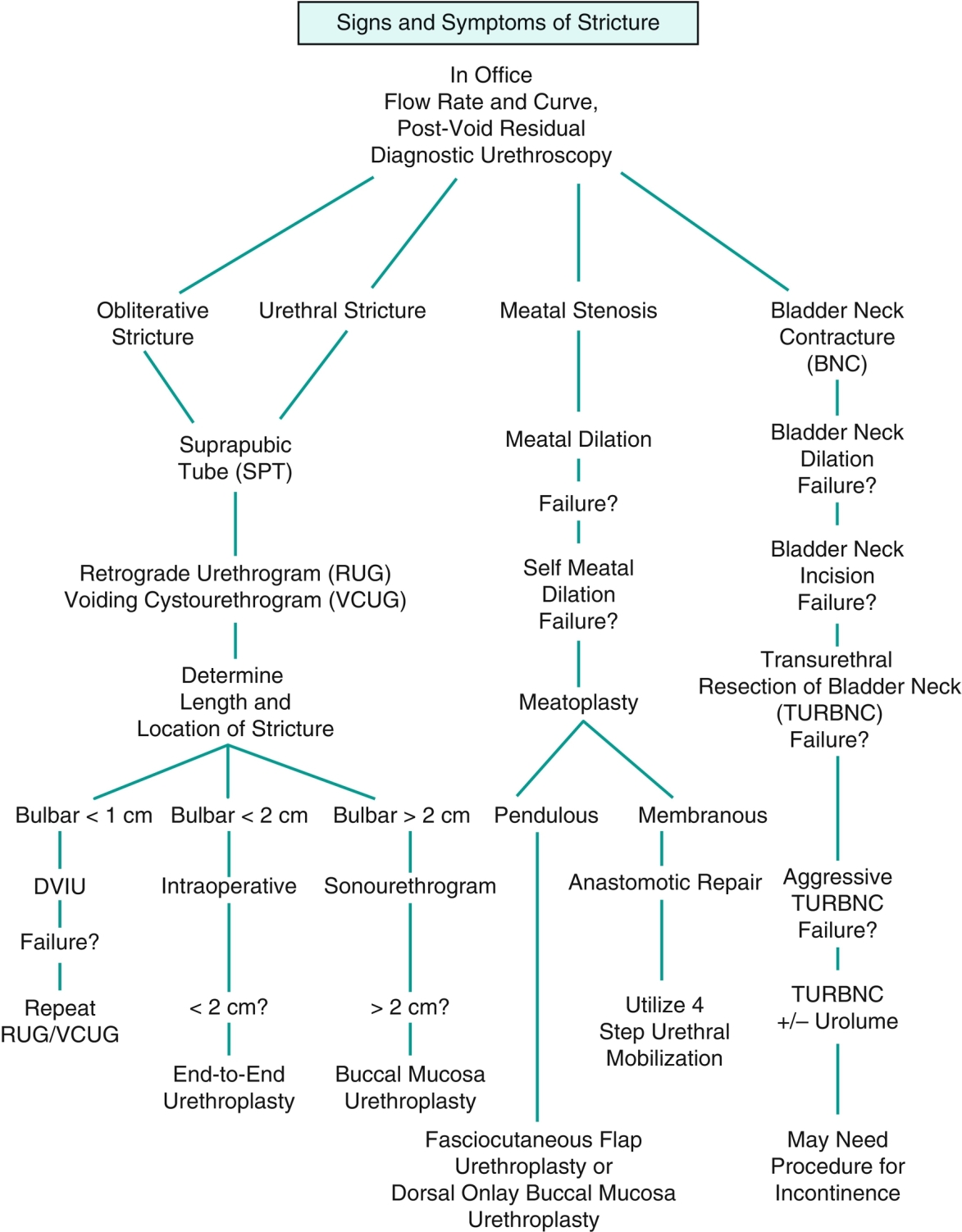
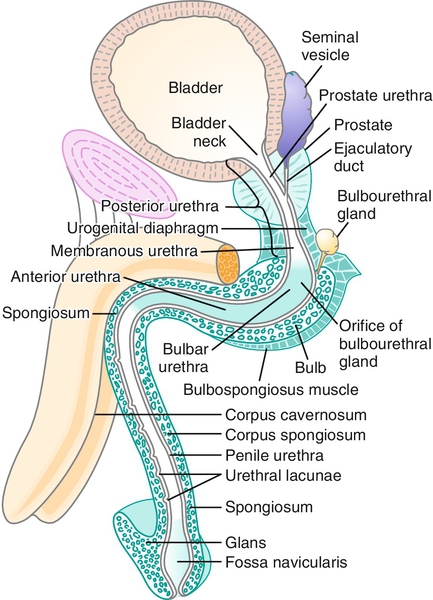
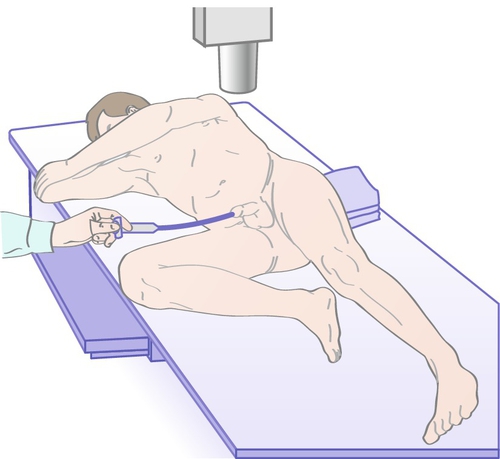
Chapter 11 2. The anterior urethra begins at the urogenital diaphragm and includes the bulbar urethra, the penile or pendulous urethra, and the fossa navicularis and meatus. 3. The posterior urethra includes the prostatic and membranous urethra (Figure 11-1). b. Penetrating injuries can involve the penile urethra. 2. Posterior urethra 2. Other sexually transmitted diseases such as Chlamydia trachomatis can also result in stricture disease. 2. Meatal strictures can result in splaying or splitting of the urinary stream. Diagnosis is largely clinical, based on history. Clinical suspicion can be supported by a flow rate and curve determination and/or assessment of postvoid residual. The shape of the flow curve is as important as or more important than the actual rate measurement. A “plateau” pattern, in which the flow rate reaches a rate and continues at this rate and no faster, is indicative of an obstructive process in the urethra. 2. The patient should be placed obliquely at 30 to 45 degrees, with the bottom leg flexed 90 degrees at the knee and the top leg straight. This allows unobstructed lateral imaging of the urethra and limits imaging foreshortening, which occurs with anteroposterior projection. 3. A 12- or 14-F Foley catheter is then placed within the fossa navicularis, and the balloon is inflated with 2 mL of saline to prevent dislodgment. 4. Contrast is then injected by the way of the catheter to opacify the urethra, and images are obtained. 5. In some cases, a voiding study is required to fully evaluate the stricture, especially in proximal lesions. The bladder is filled in a retrograde fashion via this catheter, or a small feeding tube (5 or 8 F) can be navigated through the stricture to allow for bladder filling. This component of the study can show what aspect of the urethral stricture is truly urodynamically significant as proximal dilation and distal diminution of urethral caliber will be seen (Figure 11-2). 2. Periurethral abscess proximal to distal obstruction from the urethral stricture 3. A urethral diverticulum can form proximal to the site of obstruction and cause postvoid dribbling or infections. 2. Algorithm for treatment (Table 11-1) 3. Urethral dilation can be performed in the office with local anesthesia with lidocaine jelly and is still a mainstay of therapy for stricture disease. A well-performed dilation may be the least traumatic of all of the minimally invasive techniques. Urethral sounds or filiforms and followers can be employed to perform the dilation. Both techniques are not without risks, however. Urethral false passages and trauma can lead to development of longer and more complex strictures. Urethral dilation should be considered a palliative procedure as definitive successes are extremely rare. 4. A combination of flexible endoscopy and filiform placement can be a valuable tool to ensure correct luminal placement of the filiform. The filiform, placed in parallel next to the scope, is seen to transverse the stricture as opposed to a passage based on feel. 5. Soft dilation is a practice of the placement of a urethral catheter that is changed and increased in size over a period of days or weeks. This has not resulted in long-term success but can atraumatically extend the life of a dilation. 6. Direct vision incisional urethrotomy (DVIU) b. A variation of the aggressive DVIU incision at the 12 o’clock position is multiple small, shallow incisions in a stellate pattern—the radial DVIU. Theoretically, this causes less damage and may result in a recurrence that is only minimally longer and more complex than the original stricture, making formal open urethroplasty easier to perform. c. Urethrotomies with a hot knife or a laser should be avoided, secondary to the addition of thermal injury to the spongiosal tissue making recurrences longer and more severe. d. Results
Urethral Stricture Disease
Definition
Etiology
Trauma
Iatrogenic
Infection
Clinical presentation
Obstruction
Secondary complications
Diagnosis
Urethroscopy
Retrograde urethrogram (RUG) and voiding cystourthrogram (VCUG)
Associated conditions
Treatment
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree