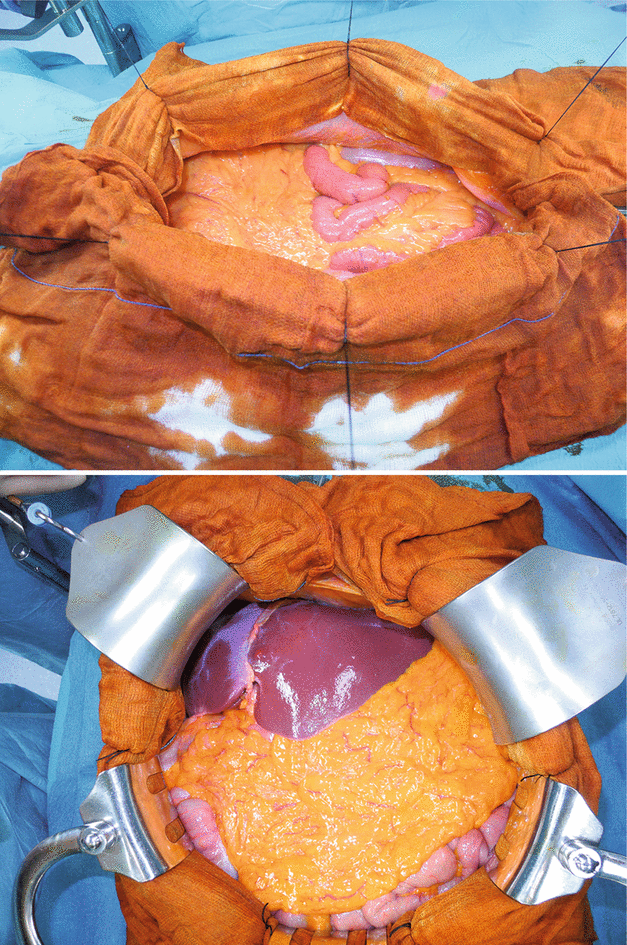
Figs. 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3
After having disinfected the operating field by passing in succession two gauze pads soaked in povidone-iodine (or benzalkonium chloride if the patient is allergic to iodine), a midline incision from the xiphoid process to below the umbilicus is the most common approach for total and subtotal gastrectomy in patients with normal stature and weight. To minimize the risk of operation site infection, a gauze laparotomy pad soaked in povidone-iodine or benzalkonium chloride should be secured to either side of the incision with three full-thickness sutures, to protect the tissue layers in direct contact with the operating field. The operative field is exposed using Ulrich and Guarducci retractors
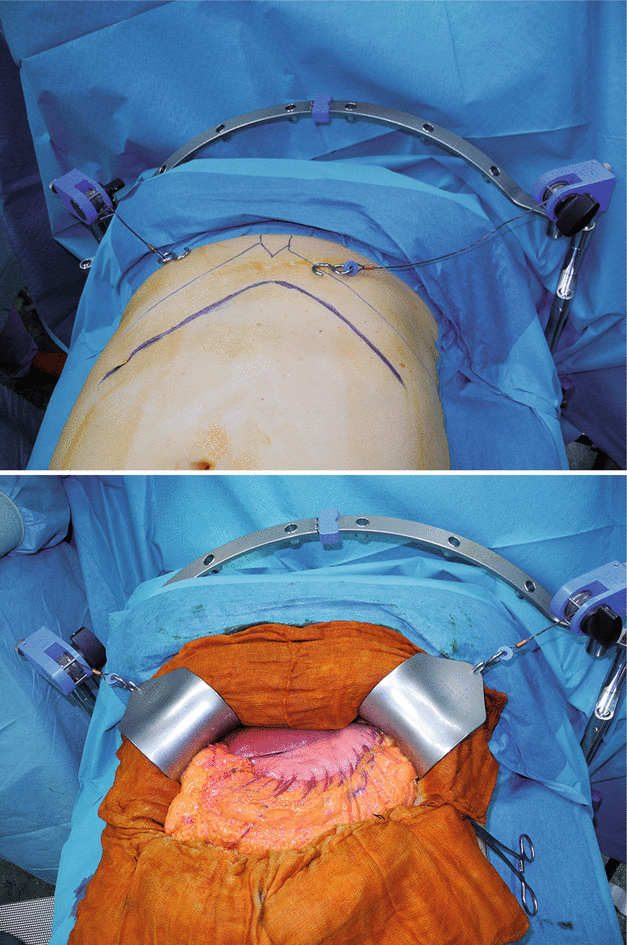
Figs. 2.4 and 2.5
A bilateral subcostal incision provides better exposure in short and obese patients and in esophagocardial tumors. The operative field is exposed using Ulrich or Kent or Rochard retractors
2.2 Exploration of the Abdominal Cavity and Lavage Cytology

Fig. 2.6
If no nodules of omental or peritoneal carcinosis are detected, but free fluid is found in the supramesocolic space, a sample of this is collected and submitted for intraoperative cytology. Otherwise, peritoneal lavage is performed with ca. 100 ml of saline poured upstream of the gastric wall involved by the neoplasm; the fluid is then recovered for intraoperative cytology
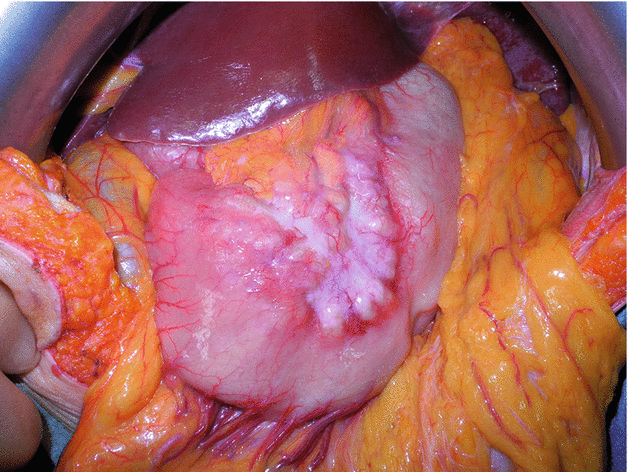
Fig. 2.7
An example of locally advanced gastric tumor massively involving the lesser curvature and adjacent lymph nodes
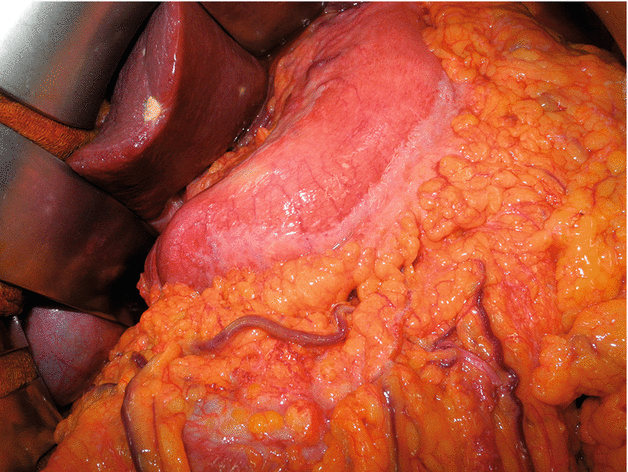
Fig. 2.8
An example of gastric “linitis plastica,” a diffuse intramurally infiltrating type of cancer in which the neoplastic cells invade throughout the stomach, resulting in the thickening and rigidity of the stomach wall. This stiff walled organ is also called “leather bottle stomach”
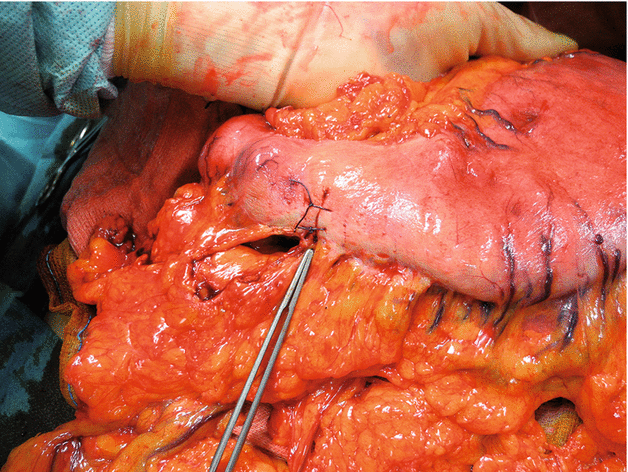
Fig. 2.9
Since diagnosis of gastric “linitis plastica” through endoscopic biopsies is frequently difficult to obtain, an intraoperative full-thickness gastric wall biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of malignancy
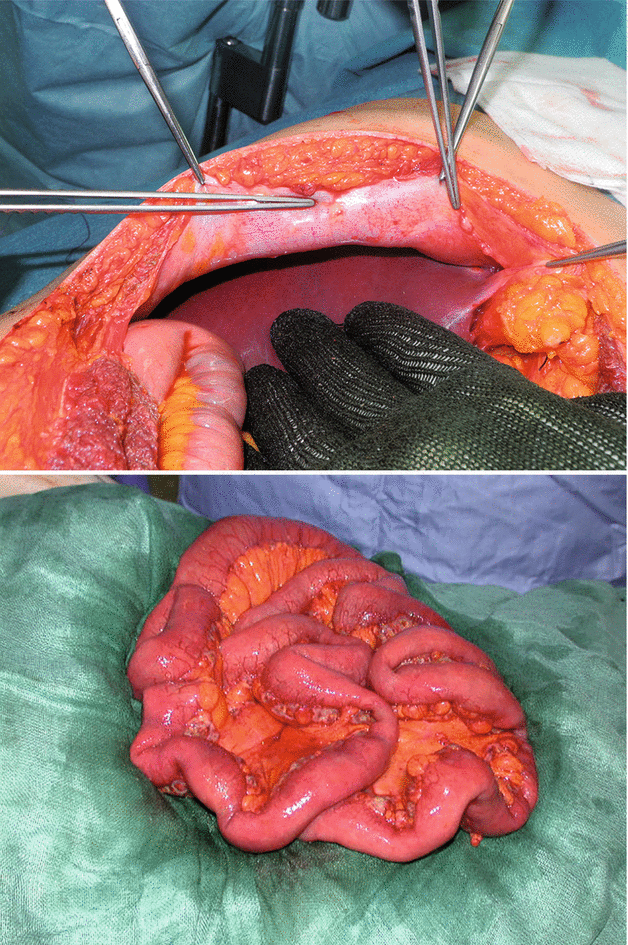
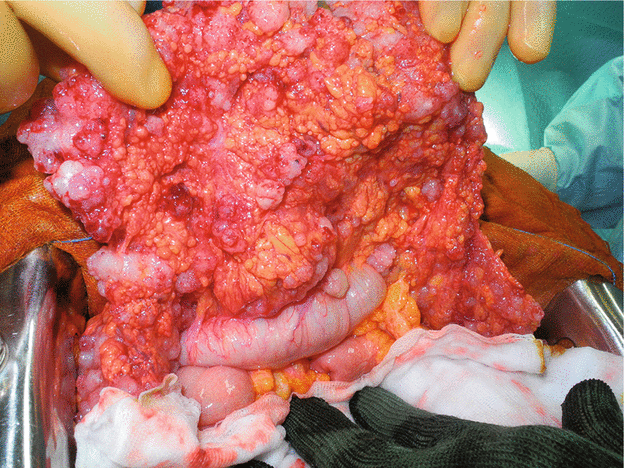
Figs. 2.10, 2.11, and 2.12
The supra- and inframesocolic spaces are explored for nodules of peritoneal, visceral, and omental carcinosis
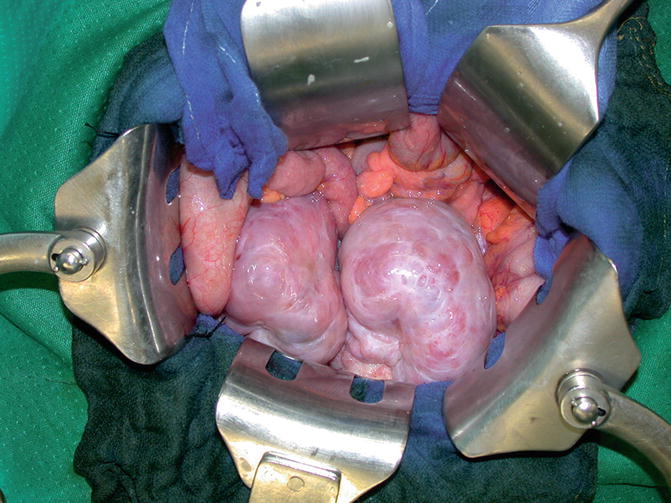
Fig. 2.13
In female patients the ovaries are inspected to exclude metastatic disease (Krukenberg tumor)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








