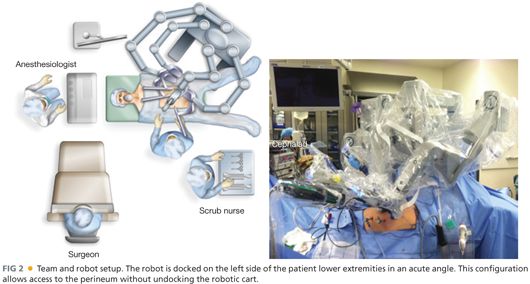
■ Optimal modified lithotomy position is crucial to ensure adequate perineal access while allowing appropriate robotic side docking (see the following text) to avoid external robotic arm conflict (FIG 2).
TECHNIQUES
INCISION, PORT PLACEMENT, AND INSTRUMENTS
■ A total of five ports are used for robotic-assisted APR: two 12-mm ports for the robotic camera and assistant (the latter is for use with laparoscopic instruments) and three 8-mm ports for robotic instrumentation.
■ The robotic camera port is placed in the periumbilical region and the assistant port in the right upper quadrant. The 8-mm instrument ports are placed in the right and left lower quadrants and in the left upper quadrant (FIG 3).
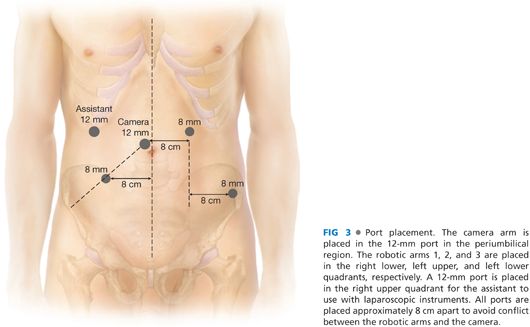
■ The ports are placed approximately 8 cm apart to prevent conflict between the robotic arms and the camera.
EXPLORATION AND ROBOTIC DOCKING
■ The abdominal cavity is assessed and, in oncologic cases, the presence of distant metastases is evaluated.
■ Lysis of adhesions is performed laparoscopically, if needed.
■ The patient is positioned in a steep Trendelenburg position with the left side elevated 15 degrees. The small bowel and omentum are retracted out of the pelvis.
■ The robot is docked on the left side of the patient’s lower extremities in an acute angle (FIG 2). The camera arm is placed in the 12-mm port in the periumbilical region, whereas the robotic arms 1, 2, and 3 are placed in the right lower, left upper, and left lower quadrants, respectively (FIG 3).
ESTABLISHMENT OF THE PRESACRAL PLANE
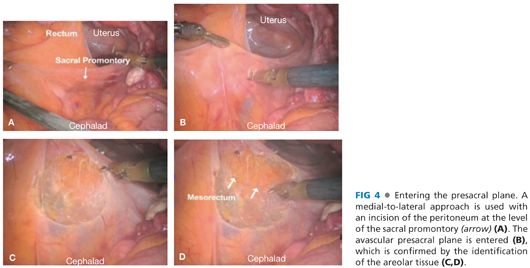
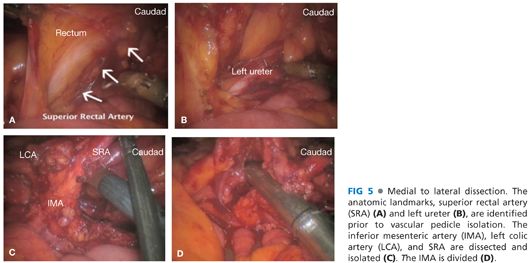
■ A medial to lateral approach is used with an incision of the peritoneum at the level of the sacral promontory. The avascular presacral plane is entered, which is confirmed by the identification of the areolar tissue (FIG 4). This plane is developed identifying the superior rectal artery and the left ureter (FIG 5). The vascular pedicle is isolated, identifying the inferior mesenteric artery, superior rectal artery, and the left colic artery (FIG 5).
VASCULAR DIVISION
■ At this point, the inferior mesenteric artery is ligated at its origin from the aorta using a laparoscopic stapler, electrosurgical device, or clips (FIG 5).
MESORECTAL DISSECTION
■ Attention is drawn to the pelvis for the mesorectal excision. The pelvic dissection proceeds posteriorly first, then laterally, and then anteriorly.
■ First, the avascular presacral plane is entered for the posterior dissection. Arm 3 is used for retraction, whereas arms 1 and 2 develop a plane of dissection within the avascular presacral space between the presacral fascia, posteriorly, and the mesorectal fascia, anteriorly. Arm 2 of the robot (left hand of the surgeon) should avoid grasping the mesorectum, for the strong robotic arm may tear the mesorectum, which would cause bleeding.
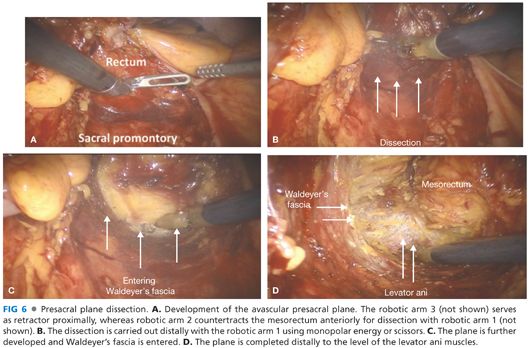
■ The fascia propria of the rectum is identified and preserved with sharp dissection using the robotic scissors or monopolar device. Dissection continues in the posterior mesorectal plane through the retrorectal (Waldeyer’s) fascia to the level of the anorectal junction (FIG 6).
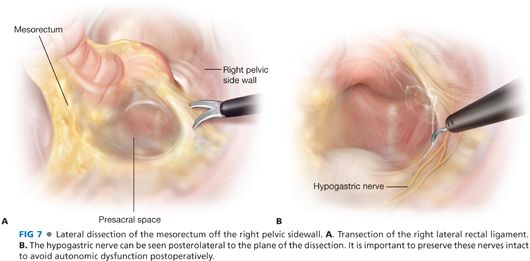
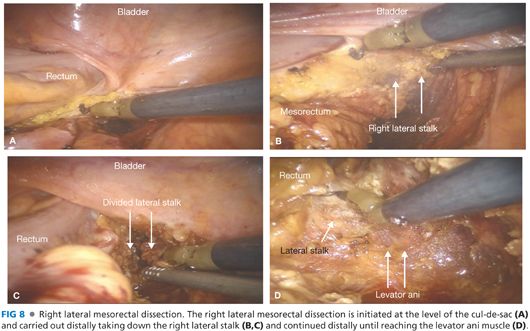
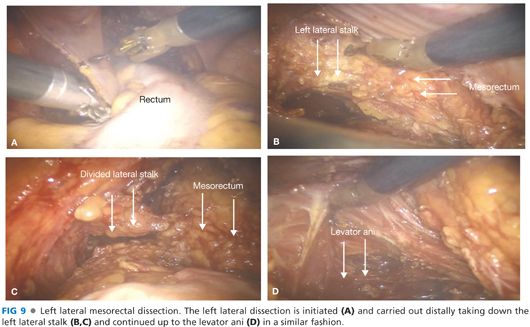
■ The lateral mesorectal dissection follows (FIG 7). The hypogastric nerve can be seen posterolateral to the plane of the dissection. It is important to preserve these nerves intact to avoid autonomic dysfunction postoperatively (FIG 7). Attention is first drawn to the right lateral pelvic attachments, which are divided starting at the level of the anterior peritoneal reflection and extending distally until reaching the levator ani muscle (FIG 8). The left lateral rectal ligament is then transected in a similar fashion (FIG 9).
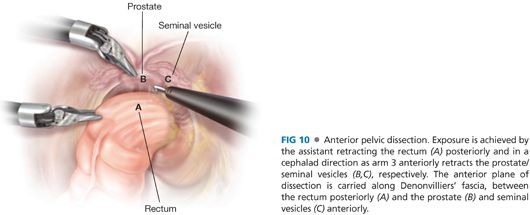
■ Lastly, the anterior mesorectal dissection is performed (FIG 10).
■
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








