Algorithm 18.1 Investigations for suspected metabolic disease
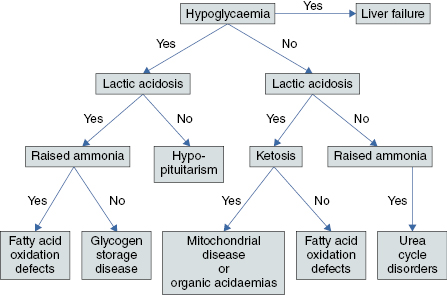
Table 18.1 Differential diagnosis, investigations, treatment and outcome of acute liver disease presenting in neonates
| Differential diagnosis | Investigations | Specific treatment and outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Herpes simplex | Blood and urine PCR Immunofluorescence of vesicle swabs | Aciclovir (20 mg/kg 8 hourly for 14 days) Multisystem disease with high mortality |
| Adenovirus | Blood PCR | Cidofovir (5 mg/kg weekly, requires pre-treatment with probenicid and hyperhydration) Outcome depends on severity of viral infection |
| ECHO virus | Stool PCR | Supportive, liver transplant Survival depends on severity of viral infection |
| Coxsacchie virus | Stool PCR | Supportive, liver transplant Outcome depends on severity of viral infection |
| Parvovirus | Blood PCR | Supportive, liver transplant Survival depends on severity of viral infection |
| Neonatal haemochromatosis | Lip biopsy: iron in salivary glands MRI T2 images: high iron content of pancreas and liver as compared to spleen | Antioxidant cocktail, plamapheresis and immunoglobulins (medical management only effective in mild cases), liver transplantation |
| Mitochondrial disease | High blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lactate Muscle biopsy (fat droplets and ragged red fibres) Mitochondrial DNA from blood, liver or muscle EEG | Multisystem progressive life-limiting disease Liver transplant is contraindicated Palliative care |
| Galactosaemia | Reducing substances in urine, galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase | Lactose free diet Long-term stabilisation on diet, but learning difficulties and infertility are common |
| Urea cycle disorders | Raised ammonia Plasma amino acids | Emergency management of hyperammonaemia: see Red flags Hepatocyte transplant as a rescue therapy Maintenance treatment: protein restricted diet Liver transplant for complications Most neonates die at first presentation or have neurological abnormalities Lifelong risk of hyperammonaemia coma |
| Fatty acid oxidation defects | Acyl carnitines, low carnitine, lactic acidosis, raised ammonia, raised creatinine kinase | Avoid fasting using nasogastric feeding and cornstarch 60% mortality at presentation In those who survive, long-term outcome is good |
| Organic acidaemias | Acidosis, hyperammonaemia, urine organic acids | Emergency treatment of hyperammonaemia (see Red flags) Correct hypoglycaemia and acidosis, carnitine (200 mg/kg/day) and metronidazole (20 mg/kg/day) in the acute illness Maintenance with low protein, high calorie diet Vulnerable to the development of neurological disease, stroke, basal ganglia changes and developmental delay in childhood. Liver transplant in early childhood may prevent neurological deterioration. |
| Carbohydrate deficient glycoprotein (CDG) defect | Transferrin electrophoresis DNA |




