 Red flags: When to be concerned about jaundice
Red flags: When to be concerned about jaundice- Any infant who has persistent jaundice after 2 weeks should have a split bilirubin test to distinguish between unconjugated and conjugated jaundice
- Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia indicates liver disease requiring referral to a liver specialist centre for urgent investigation.
Important features from history
- Family history of jaundice, neonatal deaths or miscarriages
- Low or normal birth weight, failure to thrive or weight loss
- Poor feeding and irritability
- Hypoglycaemic episodes
- Vitamin K deficiency with bleeding
Examination
- Babies with significant liver disease may have a normal birth weight and normal physical examination
- Dysmorphic features, arthrogryposis, cutaneous haemangioma
- Cardiac murmur
- Enlarged spleen: always an abnormal sign
- Ascites
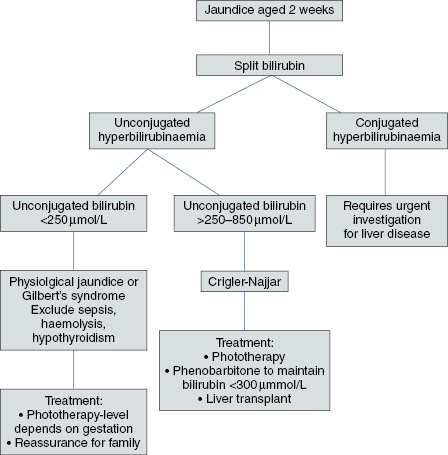
Investigations (Algorithm 17.1 and Algorithm 17.2)
The differential diagnosis and investigations for causes of unconjugated jaundice are shown in Table 17.1 and causes of conjugated jaundice are shown in Table 17.2.
Algorithm 17.1 Investigating a 2-week-old infant with jaundice
Algorithm 17.2 Investigating conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia at 2 weeks of age
Table 17.1 Differential diagnosis of unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia and recommended investigations
| Differential diagnosis | Investigation | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Physiological jaundice | Split bilirubin | Mildly raised unconjugated bilirubin |
| Breast milk jaundice | Split bilirubin | Mildly raised unconjugated bilirubin |
| Sepsis | Blood, urine, CSF culture, chest X-ray | Positive culture or changes on X-ray |
| Haemolysis | Full blood count LDH Reticulocyte count Haptoglobins | Anaemia with fragmented red cells Raised LDH High reticulocyte count Low haptoglobins |
| Hypothyroidism | TFTs | High TSH Low T4 |
| Pyloric stenosis | Ultrasound scan | Thickening of the gastric pylorus muscle. Excessive gastric peristalsis |
| Gilbert’s syndrome | Split bilirubin | Mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia |
| Crigler–Najjar I and II | Split bilirubin | Significantly raised unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia requiring treatment (see Algorithm 17.1) |
CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; TFT, thyroid function test; TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





