Investigations
- Blood count, renal, liver and bone biochemistry
- Inflammatory markers, e.g. ESR, CRP
- Immunoglobulins A/G/M/E
- Specific IgE levels to food antigens: milk/soya/egg/wheat/nuts/ fish
- Coeliac serology:
- IgA tissue transglutaminase
- Endomysial antibody
- HLA-DQ2/DQ8
- IgA tissue transglutaminase
- Stool analysis:
- Bacterial, viral and parasite examinations
- Calprotectin: a neutrophil protein stable in stool. Although specificity is suboptimal, a negative result reassures that inflammatory bowel disease is unlikely
- Bacterial, viral and parasite examinations
- Small bowel imaging (Figure 10.2):
- Magnetic enterography with oral and intravenous contrast
- Barium meal and follow-through (± per-oral pneumocolon)
- Ultrasound scanning: bowel wall thickness, increased vascularity, mass
- Magnetic enterography with oral and intravenous contrast
- Investigative dietary trials:
- Lactose-free diet
- Hypoallergenic diet
- Lactose/sucrose/fructose breath tests (poor sensitivity and specificity)
- Endoscopy: oesophago-gastro-duodenoscopy and ileocolonoscopy with biopsies (Figure 10.3)
- Lactose-free diet
Figure 10.2 (A) Barium radiology showing bowel loop separation and ‘rose-thorn’ ulceration of the terminal ileum and right colon in Crohn’s disease. (B) Magnetic resonance enterography provides imaging of the lumen, mucosa and bowel wall. A thick-walled narrow diseased segment in the right iliac fossa, with an area of pseudosacculation abutting the bladder (high signal from contrast in the lumen) and bowel loop separation with fat-wrapping (low signal).
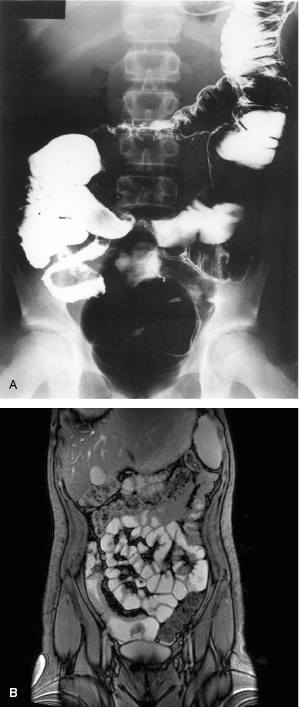
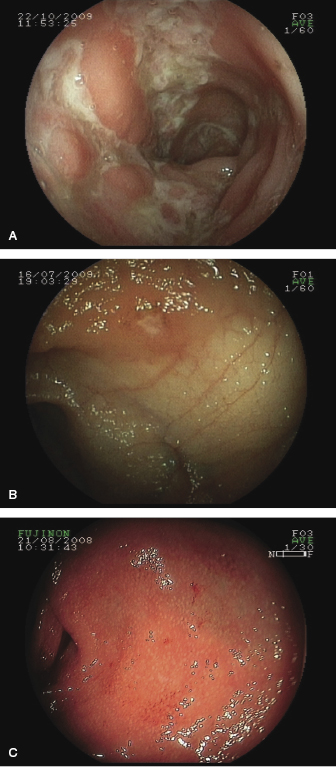
Figure 10.3 Endoscopic appearances of lesions in inflammatory bowel disease. (A,B) Crohn’s disease deep linear ‘snail-track’ ulcers (A) or apthous ulcers (B). (C) Ulcerative colitis is typically diffusely red with bleeding and ‘grains of salt’ granularity.
 Red flags: Pitfalls in the diagnosis of diarrhoea
Red flags: Pitfalls in the diagnosis of diarrhoea- Spurious diarrhoea in functional constipation with incomplete rectal emptying
- Anaemia, raised inflammatory markers and/or low serum albumin suggest inflammatory bowel disease
- Malnutrition is common in Crohn’s disease, including deficiency of iron, vitamin B12, vitamin D and zinc
Management
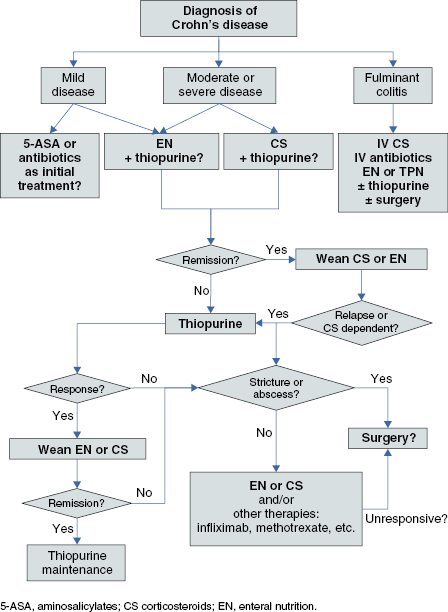
Crohn’s disease (see Algorithm 10.1)
Inducing remission
- Exclusive enteral nutrition, for 6–8 weeks to induce remission:
- Patient acceptance limits its use
- Polymeric feeds are more palatable then elemental formulae
- Nasogastric tube feeding can be a solution in some cases
- Patient acceptance limits its use
- Systemic corticosteroids:
- Administered parentally in severe disease, e.g. IV methyprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg (max 60 mg) per day or hydrocortisone 2 mg/kg (max 100 mg) qid
- Supplemental nutrition is often required by NG tube
- Specific nutrient deficiencies are common, e.g. iron, vitamin D, zinc
- Administered parentally in severe disease, e.g. IV methyprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg (max 60 mg) per day or hydrocortisone 2 mg/kg (max 100 mg) qid
Algorithm 10.1 Management of Crohn’s disease
Disease relapse
- Exclusive enteral nutrition for 6–8 weeks and oral corticosteroids are both effective in 60–80% of cases
- Active perianal disease: metronidazole 7.5 mg/kg/dose tds and/or ciprofloxacin 5 mg/kg/dose bd
Information: Exclusive enteral nutrition liquid diet therapy
- Polymeric (whole protein) or elemental (amino acid) liquid diet formula with remission is usually attained within 1–2 weeks, is effective for luminal, oral and perianal disease
- Efficacy can be affected patient and parent choice, compliance, palatability
- Has added benefits of avoiding corticosteroid toxicity and improved nutritional status
- Most children need approximately 120% of estimated average energy requirement for age. This however needs to be adjusted according to individual needs and dietetic support is essential
- Food re-introduction over 1–3 weeks, dependent on patient symptoms
Information: Corticosteroid therapy for Crohn’s disease
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




