Fig. 4.1
Routine scan of HCC
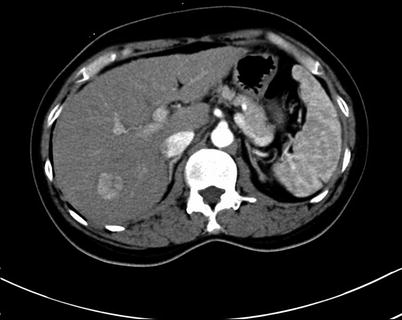
Fig. 4.2
Arterial phase images of HCC
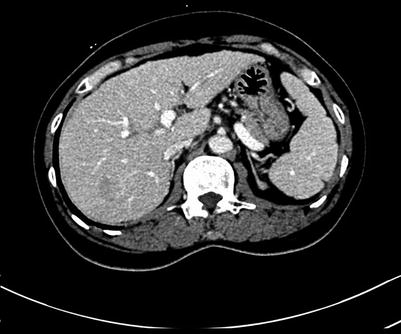
Fig. 4.3
Portal venous and arterial phase images of HCC
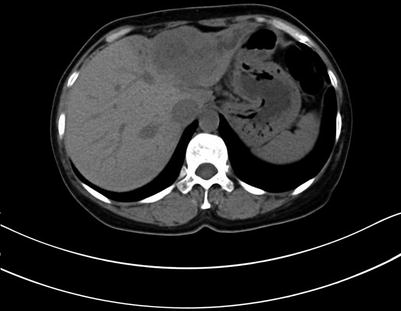
Fig. 4.4
Routine scan of ICC
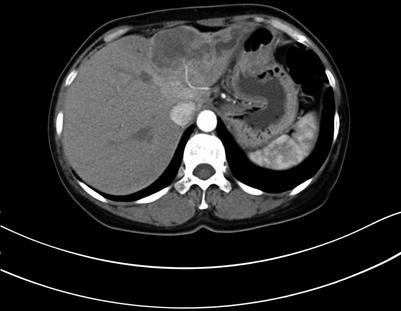
Fig. 4.5
Arterial phase images of ICC
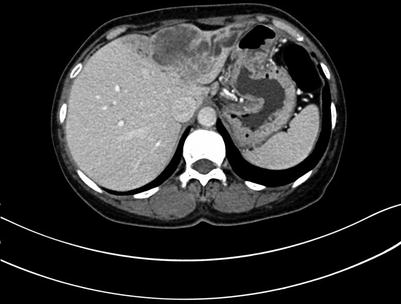
Fig. 4.6
Portal venous images of ICC
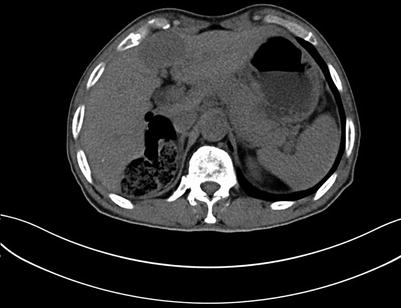
Fig. 4.7
Routine scan of liver hemangioma
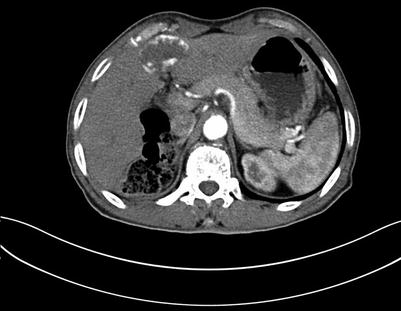
Fig. 4.8
Arterial images of liver hemangioma
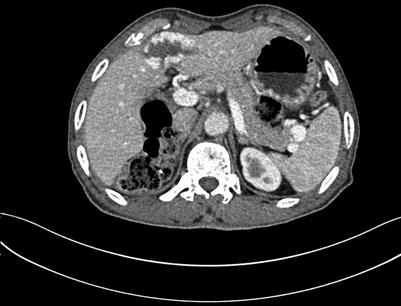
Fig. 4.9
Portal venous images of liver hemangioma
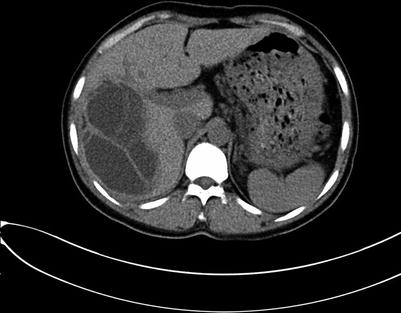
Fig. 4.10
Routine scan of liver hydatid
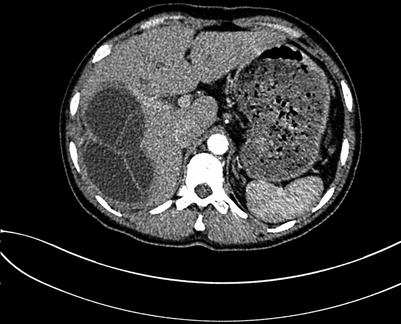
Fig. 4.11
Arterial phase images of liver hydatid
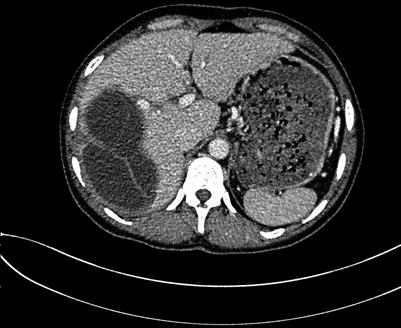
Fig. 4.12
Portal venous images of liver hydatid
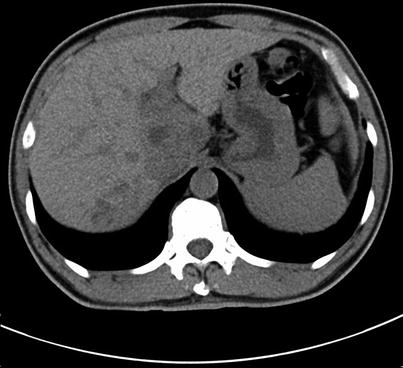
Fig. 4.13
Routine scan of hepatic pulmonary fluke
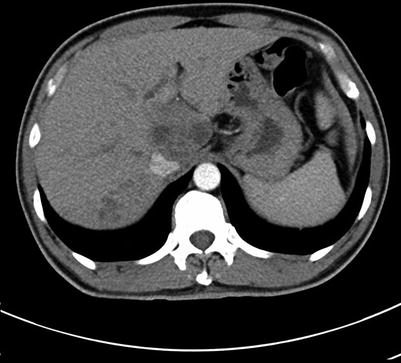
Fig. 4.14
Arterial phase images of hepatic pulmonary fluke
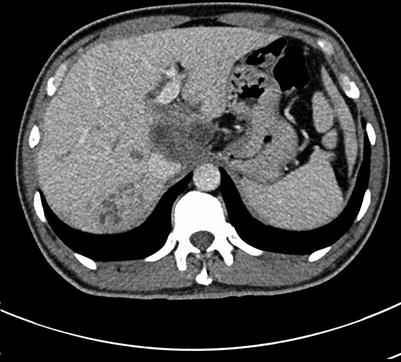
Fig. 4.15
Portal venous images of hepatic pulmonary fluke
4.1.1 The Application of 3D Reconstruction in Hepatectomy
A 3D reconstruction provides a comprehensive display of the anatomical location of the lesions. This method shows the relationship between the lesions and the vasculature (including the hepatic artery, portal vein, hepatic vein, and inferior vena cava (IVC)), hilar bile duct, diaphragm, and gastrointestinal tract (Figs. 4.16, 4.17, 4.18, 4.19, and 4.20). Because the anatomy adjacent to the liver is complicated, care should be taken to differentiate between (i) the bare area of the right lobe of the liver and the right adrenal or perirenal glands (Figs. 4.21, 4.22, 4.23, 4.24, and 4.25); (ii) the left lobe of the liver and the stomach, the liver-stomach interface, and the spleen (Figs. 4.26, 4.27, 4.28, 4.29, 4.30, and 4.31); and (iii) the caudate or left lobe of the liver and the enlarged lymph node in the portacaval space, the pancreas, and adjacent tissues (Figs. 4.32, 4.33, 4.34, 4.35, and 4.36).
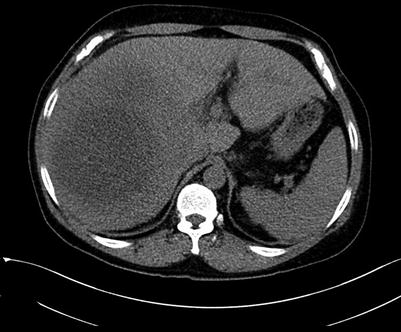
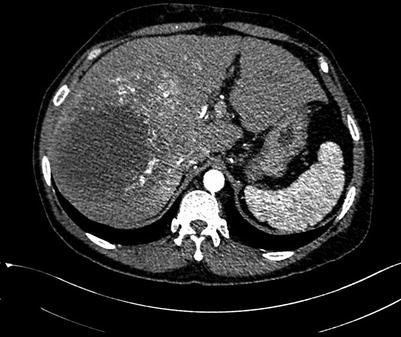
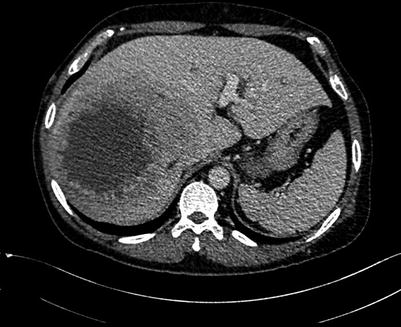
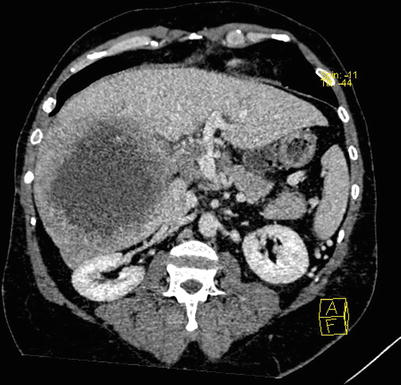
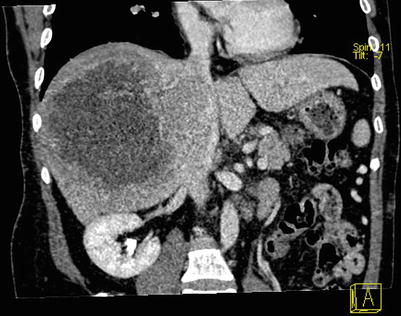
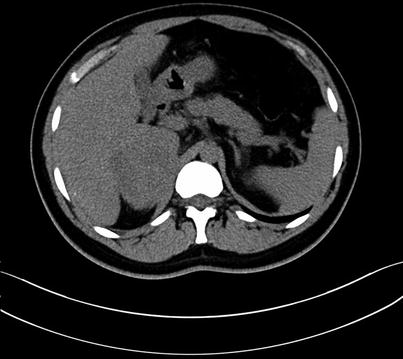
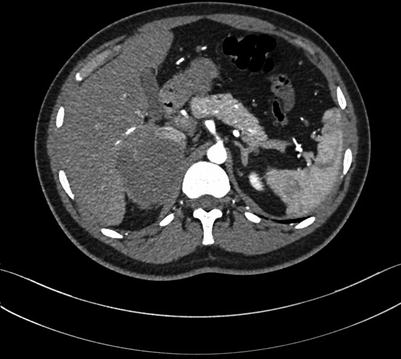
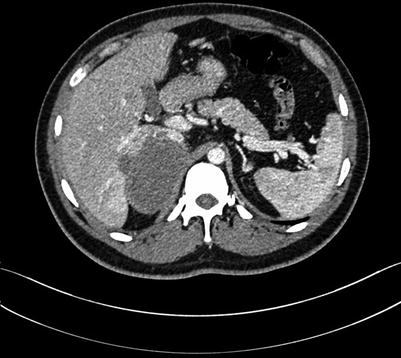
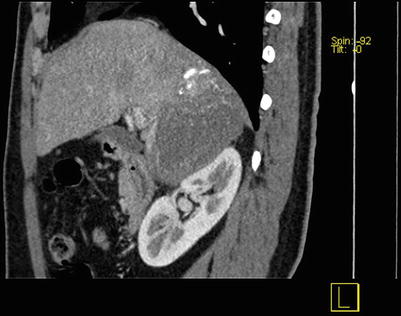
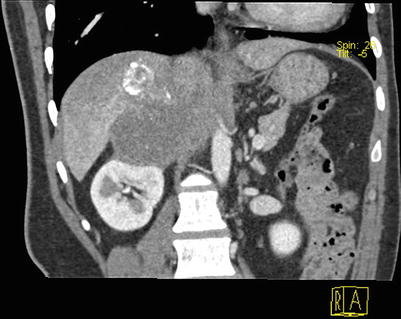
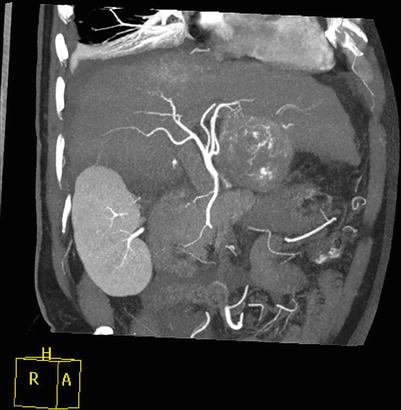
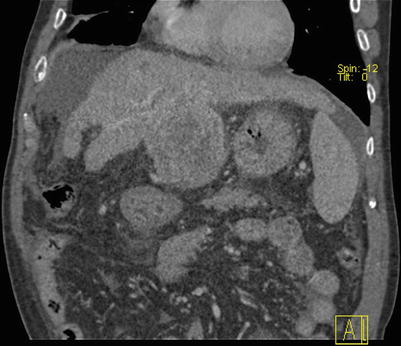
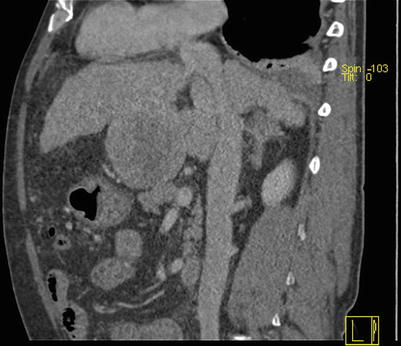
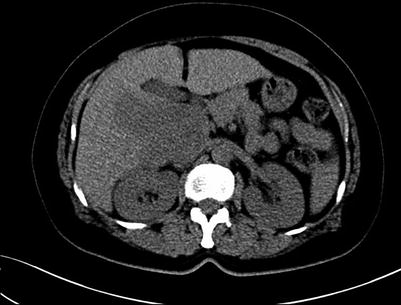
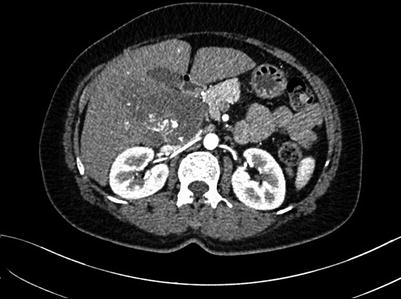
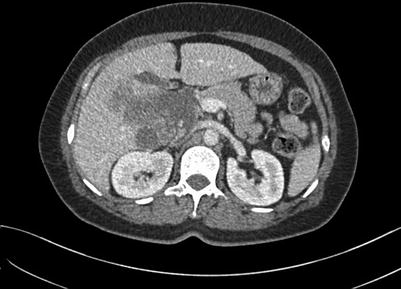
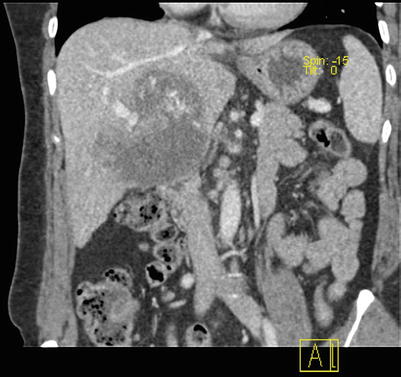
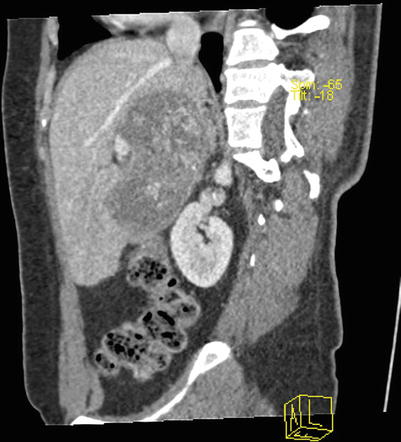

Fig. 4.16
Routine scan of HCC with thrombosis of right branch of the portal vein, while the hepatic vein and IVC suspected involvement

Fig. 4.17
Arterial phase images of HCC with thrombosis of right branch of the portal vein, while the hepatic vein and IVC (suspected involvement)

Fig. 4.18
Portal venous images of HCC with thrombosis of right branch of the portal vein, while the hepatic vein and IVC (suspected involvement)

Fig. 4.19
CT reconstruction of the right branch of portal vein thrombosis

Fig. 4.20
CT reconstruction of the right hepatic vein and IVC (suspected involvement)

Fig. 4.21
Routine scan of right lobe lesions (hydatid) involving the right adrenal gland

Fig. 4.22
Arterial phase images of right lobe lesions (hydatid) involving the right adrenal gland

Fig. 4.23
Portal venous images of right lobe lesions (hydatid) involving the right adrenal gland

Fig. 4.24
CT reconstruction of right lobe lesions (hydatid) involving the right adrenal gland

Fig. 4.25
CT reconstruction of right lobe lesions (hydatid) involving the right adrenal gland

Fig. 4.26
Routine scan of hepatic left lateral lobe lesions

Fig. 4.27
Arterial phase images of hepatic left lateral lobe lesions

Fig. 4.28
Portal venous images of hepatic left lateral lobe lesions

Fig. 4.29
MIP of hepatic left lateral lobe lesions

Fig. 4.30
Coronal reconstruction of hepatic left lateral lobe lesions

Fig. 4.31
Sagittal reconstruction of hepatic left lateral lobe lesions

Fig. 4.32
Routine scan of caudate lobe lesions

Fig. 4.33
Arterial phase images of caudate lobe lesions

Fig. 4.34
Portal venous images of caudate lobe lesions

Fig. 4.35
Reconstruction of caudate lobe lesions

Fig. 4.36
Reconstruction of caudate lobe lesions
4.1.1.1 The Anatomy of the Liver Vasculature
Hepatic artery: Imaging can reveal the origin and branch of the hepatic artery and the presence of the aberrant hepatic artery (Figs. 4.37 and 4.38).
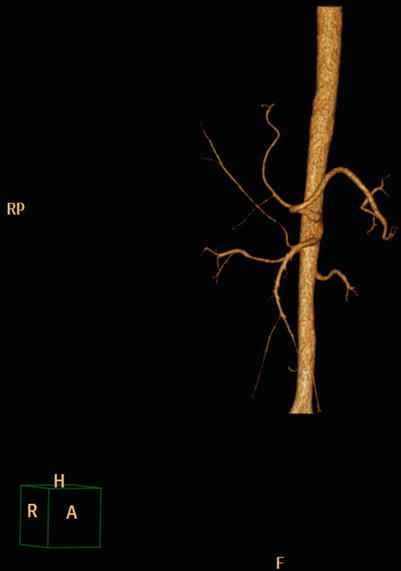

Fig. 4.37
3D image of the right hepatic artery from the superior mesenteric artery

Fig. 4.38
3D image of the left hepatic artery arises from the left gastric artery
Portal vein: Imaging shows the branch characteristics of the portal vein, including the left and right branches or the left middle and right branches. The branch and the blood supply area are also observed (Figs. 4.39, 4.40, and 4.41).
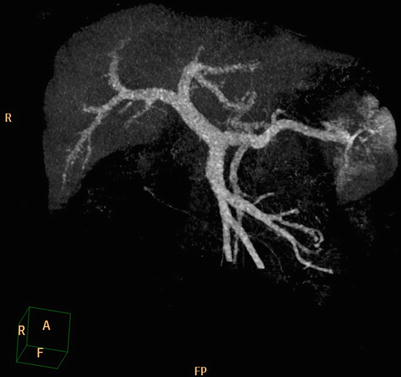
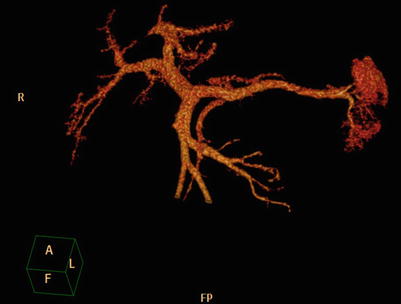

Fig. 4.39
Reconstruction of the left and right and intrahepatic branches and the blood supply area

Fig. 4.40
MIP of the left and right and intrahepatic branches and the blood supply area

Fig. 4.41
VR of the left and right and intrahepatic branches and the blood supply area
Hepatic vein: Imaging reveals how the left, middle, and right hepatic veins empty into the IVC, including the three hepatic vein confluences and the left and right hepatic vein confluence (Figs. 4.42 and 4.43). Moreover, common anatomic variations include an accessory right hepatic vein in the first hepatic portal plane, where there is commonly only one (Fig. 4.44). Multiple hepatic vein scan empty into the IVC in the second hepatic portal plane. The hepatic venous drainage area can be accurately determined in cross-sectional images (Fig. 4.45).
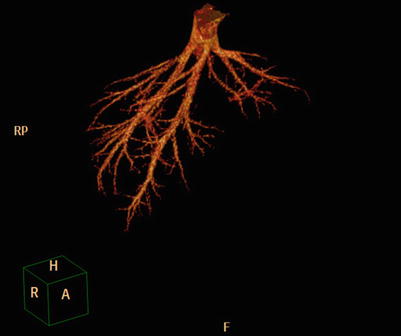

Fig. 4.42




VR of three separate veins draining into IVC
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







