Fig. 10.1
The difference between conventional laparoscopic surgery (a) and SPLS (b)
10.2 Types and Characteristics of Access Ports
Usually, a trans-navel approach is chosen. This approach consists of a method that uses a platform exclusively applied in a SPLS and has several trocars inserted into a single incision.
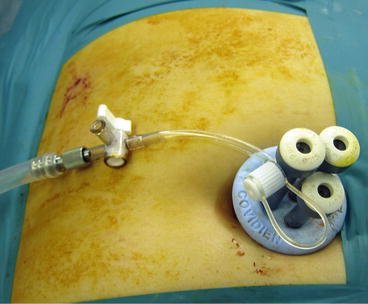
10.2.1 Multiple Trocar Method (Fig. 10.2) [1]
Fig. 10.2
Multiple trocar method
This method requires the gathering of multiple trocars that are used in conventional laparoscopic surgery in a limited space within the umbilical region. Several trocars are inserted into one skin incision. For the forceps used exclusively for tissue retraction, direct puncture insertion can also be performed. Direct insertion of the forceps is of great help to avoid interference of trocar head. On the other hand, this causes difficulty in replacing the forceps, and manipulation of the forceps is encumbered. In addition, occurrence of tissue damage should be in consideration. Usually, a common surgical method is to insert about three 5-mm trocars into the umbilical region. If trocars with large heads are used, they may interfere with one another. To avoid this issue, it is better to use a trocar with a small head or to arrange trocars of differing lengths. Once a 2-cm incision in the umbilical region and then an incision in the region between the umbilical fossa and beneath the skin is made, a space of about 2.5 to 3 cm can be obtained. With this approach, a distance of 3 cm or more between two forceps can be ensured. Moreover, if the incision is extended to about 2.5 cm, the distance between the two forceps could be 3 cm or more. Therefore, it becomes possible to operate via laparoscopy and have a feeling similar to that of performing a conventional operation. On the other hand, if the incision is too small and excessive stress is applied to the skin, the tissue could sustain injury, and wound healing could be delayed. Hence, an incision with some margin should be made. Moreover, if resection of an organ is required, it might be necessary to incise the fascia more. In that case, attention is required because if the fascial closure were performed too securely, a complicating hernia could occur.
Because a major advantage of the multiple trocar method is the greater flexibility and configurability of the distance between the two forceps, we can also use a conventional trocar or forceps; that is to say, SPLS can be performed without using special equipment. For a multiple organ resection, attention is required because a trocar positional change can be difficult once the trocar is inserted. It is difficult to always insert a trocar in the same position for various cases. Individual differences among surgeons are likely to occur. In addition, upon insertion of the first trocar, it is necessary to use the optical view trocar or to make a small incision. Moreover, manipulation proficiency is required to insert the second and third trocars safely because positional confirmation of the trocar tip is difficult.
10.2.2 Multi-Channel Port Method (Fig. 10.3) [2]