Chapter 26 PRACTICAL ISSUES IN NUTRITION AND SUPPLEMENTATION IN GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE
• In upper gastrointestinal obstruction, endoscopic techniques facilitate access to the normal functional bowel distal to the obstruction, and thus restore normal digestion and absorption. It is imperative to simultaneously decompress the stomach proximal to the obstruction when feeding distally in order to avoid secretion build-up in the stomach.
• In lower gastrointestinal obstruction, the treatment is early surgery or total parenteral nutrition (TPN).
• Intestinal adaptation to intestinal loss may take up to 2 years. Thus, strong initial support is needed to optimise conditions for adaptation.
• If less than 200 cm of small intestine without colon is present and IV supplementation becomes necessary, the condition is regarded as ‘small bowel intestinal failure’. This is also the case if less than 50 cm of small intestine remains with colon, and TPN or home TPN becomes essential for survival.
NUTRITIONAL PROBLEMS
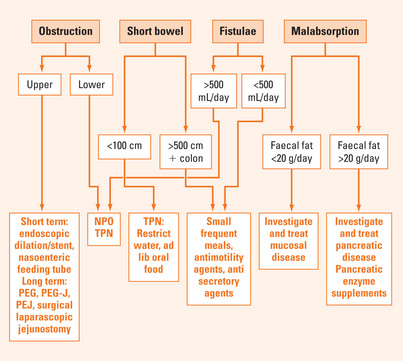
Management options for various nutritional problems are summarised in Figure 26.1.
Intestinal obstruction
Upper gastrointestinal obstruction
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree