After the basic sciences have been mastered, the student can move on to develop their psychomotor skills, beginning with a basic box trainer and moving onto the virtual reality and robotic simulator, all of which have been shown to have huge educational value [3–5].
3.8 Box Trainer
Learning of pelvic surgery should start with achieving proficiency in technical skills required in basic laparoscopic surgery using box trainer and validated curriculum of fundamentals of laparoscopic surgery (FLS). The FLS program may be effectively used to teach and assess both cognitive and technical skill aspects related to laparoscopic surgery. The simulated laparoscopic manipulation includes instrument navigation, coordination and cutting or knot-tying. It is wise to begin with the most basic of box trainers (Fig. 3.2), as if one considers simulation to be “the act of mimicking a real object, event or process by assuming its appearance or outward qualities” [6], then a box trainer is absolutely the place to start to ‘mimic’ laparoscopic surgery.
Once simple psychomotor skills such as triangulation and camera handling have been mastered, the simulation student could move on to a more Task specific box trainer. There are many versatile models (Figs. 3.3 and 3.4), which provide a range of techniques and procedural skills to be acquired over time. The anatomically and spatially realistic constraints found in this type of box trainer means that the student progresses their skills in line with the curriculum objectives that you will have set. For example, on the TURP trainer (Fig. 3.3), the student might begin with simply learning how to manage fluids during a TURP and can progress to resection of the prostate.
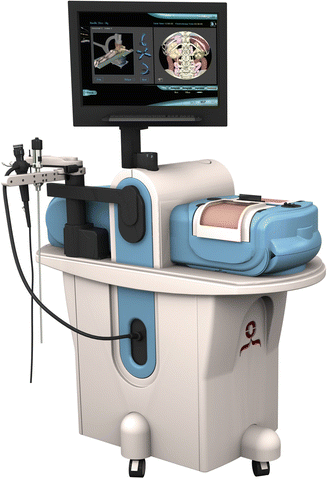
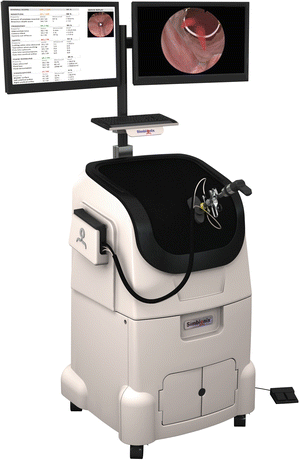

Fig. 3.3
Bristol TURP trainer

Fig. 3.4
Uro-scopic trainer
The uro-scopic trainer is a versatile model that provides for a range of urological endoscopic techniques and procedures to be acquired in line with a trainees clinical progression these skills include the following;
Fluid management
Insertion, manipulation and removal of instruments
Urethroscopy and Cystoscopy
Stent and guidewire insertion
Lithotripsy
Stone retrieval
3.9 Virtual Reality Simulator
Box trainers have their place however; a certain suspension of disbelief is required by the student in order for them to be truly effective. However, with the use of virtual reality technology the more complex procedures, along with the equally complex anatomy, can be brought to life for each student. It is through looking towards other professional areas such as airline pilots or even piano players that it was discovered that, to become what the lay person might consider an “expert,” requires 10,000 h or 10 years of practice [7] and that to maintain this level of skill requires our students not to simply be “in the job” but in fact a new concept in surgical training—deliberate practice [8–10]. The implication is that having spent hours and hours on a box trainer, mastering basic skills, there needs to be a way on which our students can spend similar amounts of time mastering more complex procedures—from beginning to end. The answer—virtual reality.
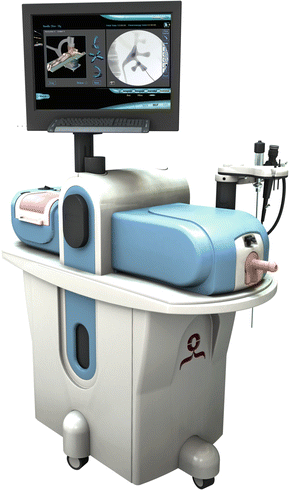
The Mentor System by Simbionix (Fig. 3.5) is one such system, with the following possible
1.
LAP Mentor™.
2.
URO Mentor™,
3.
VirtaMed TURPSim
4.
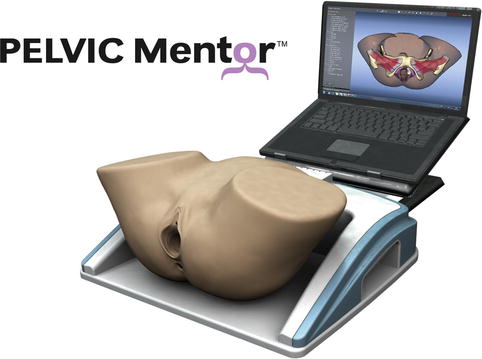
PELVIC Mentor
These ergonomically designed systems allow for real-time simulation, using the same inputs the student can expect to find in an operating theater. Equally, when practicing those essential skills in your simulation center, many of these units give haptic feedback (vibration, resistance and the same) to make the experience even more lifelike.
Each system has basic modules, with psychomotor skills tested, just as with the basic box trainer. However, these units then go on to offer anatomical, physiological, technical and surgical training, second to none. It is through the acquisition of a comprehensive set of pelvic surgical skills that a student can become not only safe but confident to perform these procedures on an actual patient.
The Lap Mentor unit allows the students to develop both basic and advanced laparoscopic skills including full procedure training with the potential for challenges such as variation in anatomy and bleeding. The URO mentor allows for everything from cystoscopes and ureteroscopes to cutting strictures and fluoroscopy/C-arm control.
The PELVIC Mentor is more aimed towards pelvic floor reconstruction with an emphasis on transvaginal mesh procedures. This system was the first to train surgeons for pelvic floor repair, using its hybrid mannequin/3D visualization system.
The presence of virtual reality simulators means that the student can progress onto more advanced simulators as their skills advance, so that, for example, once they have mastered the Bristol TURP trainer, they can progress onto advanced training.
3.10 Virtamed Turpsim
The VirtaMed TURPSim, has been called “The Most Advanced Training Simulator for TURP Procedures and BPH Treatment” [11] Once the student has mastered the basics of TURPs, this system allows for revisiting these skills in a more high fidelity fashion, as well as managing complications, again, while not having to wait for a real patient, with a real complication. As with all of the previously mentioned systems, the skills begin at a basic level and progress until mastery of all skills is eventually achieved.
Of note, though you will have set up your own comprehensive curriculum, many VR systems also come with their own “in built” training curriculum, with modules that must be mastered before moving onto the next. Your younger surgeons will feel more like they are playing a computer game, having to finish one level before they can progress onto the next. This means, that with the use of this and a box trainer, they will find themselves more comfortable with:
Heavy bleeding
Capsule perforation
Verumontanum or sphincter resection
Fluid overload
However, as any educator will know, a curriculum is really of no use without assessment. All VR trainers have, in some form or another, built in tools for both feedback and assessment.
Objective Feedback Reports
The Mentor systems all allow for objective performance assessment as well as allowing the supervisor to set their own standards for things such as economy of movements or complications handling. These feedback reports are always available to both your students and yourself, so that reflection and improvement is always possible. Another feature is that all this data can be used not only for individual development but also for research and statistical analysis.
The most advanced pelvic surgeons are now performing da Vinci surgery—and so, as the skill set required for pelvic surgeons grows, so the availability of simulation equipment grows.
3.11 Training for Da Vinci® Surgery
The robotic surgery simulator made by Simbionix has instruments designed to replicate the motions of the human hand, just as with a “real” da Vinci unit. For even greater realism, the Suturing Module can be used on the genuine da Vinci console, which means your students will not only become confident with the skills but the equipment required in robotic surgery.
All of the afore-mentioned equipment means that a surgeon in training can develop psychomotor, procedural skills in an interactive and “active learning” fashion. They will be forced to respond to a multitude of situations which can include procedure selection or the decision to proceed/abort a procedure as well as the extent of their dissection, manipulation, suturing and even which components they wish to use.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree