Fig. 7.1
Port placement and surgeon’s standing position
The right pelvic nerve plexus is dissected caudally along the pelvic wall side of the plexus, and thus, the internal margin of LPLND is determined (Figs. 7.2 and 7.3). If possible, on the most caudal aspect of the plexus, the dissection can be continued to the supra-levator ani (LA) space (Fig. 7.4).
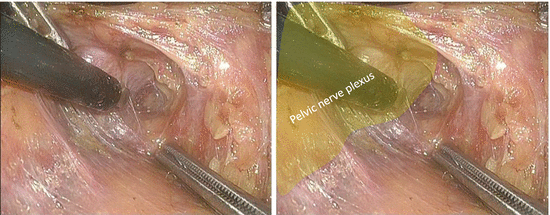
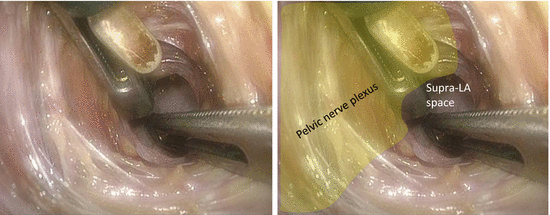

Fig. 7.2
Dissection along the pelvic wall side of the right pelvic nerve plexus − 1

Fig. 7.3
Dissection along the pelvic wall side of the right pelvic nerve plexus − 2

Fig. 7.4
Dissection along the pelvic wall side of the right pelvic nerve plexus − 3
The right ureter is separated from the surrounding tissues as caudally as possible and is pulled to the left side with a vessel tape inserted from the left inferior abdominal port.
The right external iliac artery is exposed, thereby determining the superior margin of LPLND (Fig. 7.5).
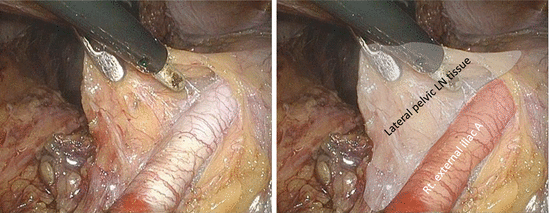

Fig. 7.5
Exposure of the right external iliac artery
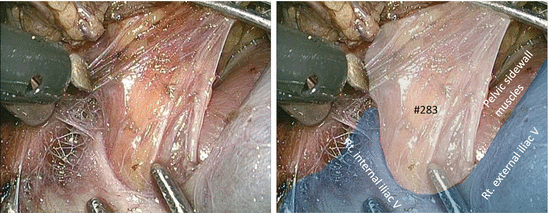
The pelvic sidewall muscles are exposed by deeper dissection along the right external iliac vein, thereby determining the lateral margin of LPLND (Figs. 7.6 and 7.7). Small vessels penetrating the pelvic sidewall should be cut meticulously with an appropriate vessel-sealing system.
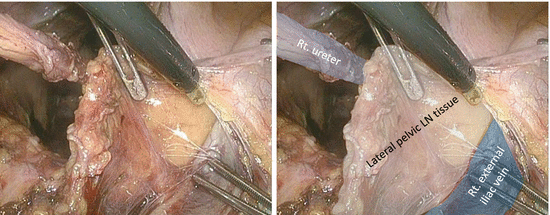
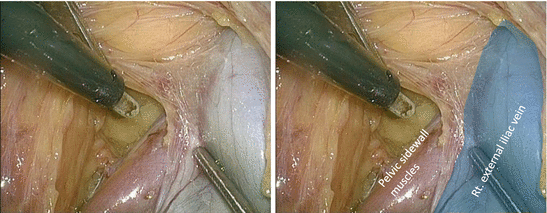

Fig. 7.6
Dissection along the right external iliac vein

Fig. 7.7
Exposure of the right pelvic sidewall muscles
The proximal portion of the lateral lymph node (LN) tissues is dissected caudally along the right internal iliac artery with the artery trunk intact (Figs. 7.8, 7.9, 7.10, 7.11, and 7.12).
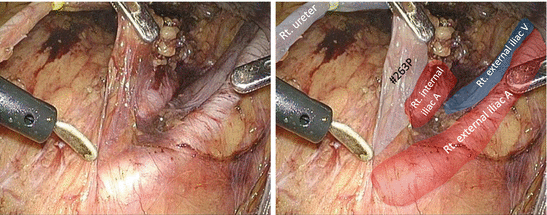
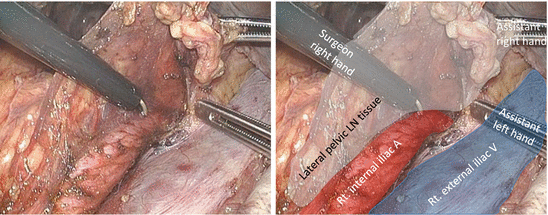
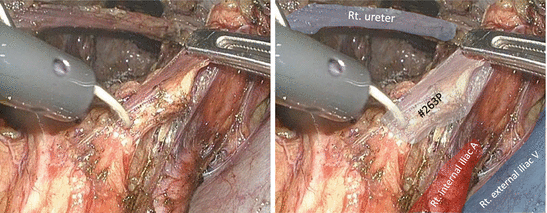
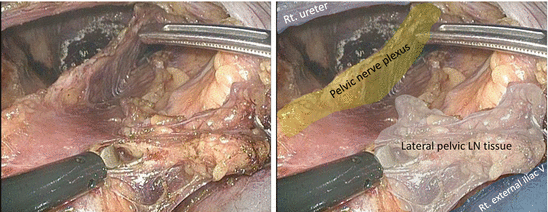
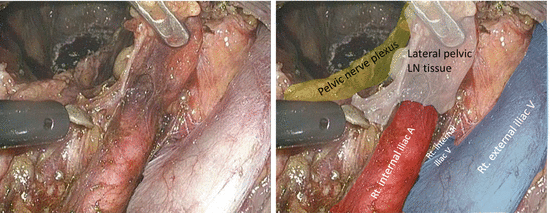

Fig. 7.8
Dissection of the proximal portion of the lateral lymph node tissues along the right internal iliac artery − 1

Fig. 7.9
Dissection of the proximal portion of the lateral lymph node tissues along the right internal iliac artery − 2

Fig. 7.10
Dissection of the proximal portion of the lateral lymph node tissues along the right internal iliac artery − 3

Fig. 7.11
Dissection of the proximal portion of the lateral lymph node tissues along the right internal iliac artery − 4

Fig. 7.12
Dissection of the proximal portion of the lateral lymph node tissues along the right internal iliac artery − 5
The right pelvic nerve plexus is preserved as a thin screen between the TME and LPLND (Fig. 7.13).
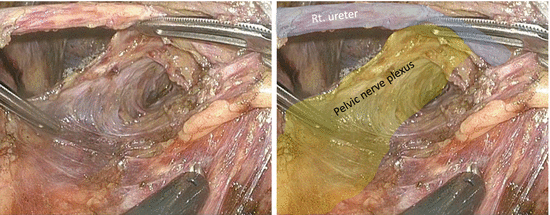

Fig. 7.13
Preservation of the right pelvic nerve plexus
The LN tissues are dissected meticulously to expose the bifurcation of the right internal and external veins (Fig. 7.14). By deeper dissection toward the pelvic sidewall, the right obturator nerve is identified and preserved (Fig. 7.15).