CHAPTER 30 EVALUATING ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
INTRODUCTION
Thrombocytopenia in the context of liver disease suggests hepatic fibrosis and impaired liver function with concomitant portal hypertension.
APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL LFTs
A detailed drug history is important including:
Liver injury may manifest several weeks after drug cessation.
Risk factors for viral hepatitis must be elicited such as injecting drug use.
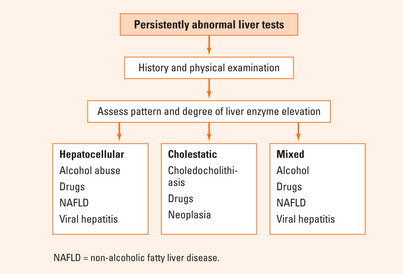
INTERPRETING PATTERNS OF LIVER TEST ABNORMALITIES
The degree and pattern of liver tests’ elevation may provide clues as to aetiology (Figure 30.1). A practically useful classification is provided below.
Liver test abnormalities are designated as:
In the vast majority of patients with liver disease, the serum ALT exceeds the AST. Exceptions include those with alcoholic liver disease and those with cirrhosis from any aetiology.
Disorders associated principally with elevations in aminotransferase levels
Common causes of liver enzyme abnormalities according to the pattern of enzyme elevation are presented in Table 30.1.
TABLE 30.1 Causes of elevated liver enzyme levels
| Hepatocellular | Cholestatic |
|---|---|
| • Excessive alcohol consumption | • Drug-induced liver injury |
| • Drug-induced liver disease | • Choledocholithiasis |
| – Chronic hepatitis B and C | • Primary biliary cirrhosis |
| – Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | • Primary sclerosing cholangitis |
| – Haemochromatosis | • Pancreatic carcinoma |
| • Autoimmune hepatitis | • Neoplastic infiltration |
| • Wilson’s disease | • Sarcoidosis |
| • Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency |
Additional laboratory tests useful in identifying specific disorders are listed in Table 30.2.
TABLE 30.2 Laboratory tests to clarify the cause of liver test abnormalities
| Laboratory test | Diagnosis |
| • Hepatitis C antibody | • Positive test suggests chronic hepatitis C infection |
| • Hepatitis B surface antigen | • Positive test suggests chronic hepatitis B infection |
| • Hepatitis B e antigen | • Positive test suggests active viral replication |
| • Serum ferritin, transferrin saturation | • Iron overload suggests haemochromatosis |
| • Antimitochondrial antibodies | • Detected in primary biliary cirrhosis |
| • Antinuclear antibodies, anti-smooth muscle antibodies | • Detected in autoimmune hepatitis |
| • Serum caeruloplasmin | • Reduced in Wilson’s disease |
| • Serum alpha1-antitrypsin | • Decreased in alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency |
Causes of elevated aminotransferase levels
Alcohol-related liver disease (ALD)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree