, Liqing Yao1 and Xinyu Qin2
(1)
Endoscopy Center, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
(2)
General surgery, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
Abstract
With the detection of more gastrointestinal caner in early stage and huge interests in minimally invasive surgery, the techniques of endoscopic resection developed and progressed rapidly. Advanced endoscopy techniques required special equipment and accessories to complete such procedures efficiently with reduces the risks of complications and trauma to the patients. This chapter introduces the equipment and accessories used for endoscopic treatment.
With the detection of more gastrointestinal caner in early stage and great interests in minimally invasive surgery, the techniques of endoscopic resection developed and progressed rapidly. Advanced endoscopy techniques required special equipment and accessories to complete such procedures efficiently with reduced risks of complications and trauma to the patients. This chapter introduces the equipment and accessories used for endoscopic treatment.
2.1 Equipment
2.1.1 Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Recent progress in endoscopic technique has made it possible to treat gastrointestinal neoplasms, and the endoscopist now confront more difficult cases, that sometimes cause complications such as bleeding and perforation. In the case of bleeding it is paramount to washout the blood to identify bleeding point. Therefore, some companies manufacture the endoscopes with waterjet function, large diameter channel and dual-channels for special treatment and to deal with the complications.
GIF-260J endoscopy from Olympus (Fig. 2.1) has the waterjet function, which can be helpful to wash the surface of the lesion to aid correct diagnosis. In addition, waterjet is frequently used to wash bleeding surface to target hemostatic treatment (Fig. 2.2). GIF-260J is also equipped with a large 3.2 mm diameter channel for the effective suction during the treatment.

Fig. 2.1
GIF-260J from Olympus with the waterjet function

Fig. 2.2
Gif-260J helps to clean away blood and blood clots, and identify the precise bleeding point
GIF-2TQ260M (Fig. 2.3) from Olympus is a multi-bending endoscope with waterjet function and 3.2 mm diameter dual channel. The multi-bending function helps approach the lesion in the “angle” and low body of stomach. For colorectal ESD, an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) endoscope may be useful because it is easy to switch to a retroflex view in the narrow space. The 3.2 mm diameter dual channel improves the operation and offers additional advantages. Firstly, a second device, such as an injection needle or a metal snare can be used simultaneously, which saves the time required to change devices.

Fig. 2.3
GIF-2TQ260M (Olympus Japan) with waterjet function and 3.2 mm diameter dual channel
Secondly, it may facilitate an easier approach to the lesion. For instance, if the operator needs to cut or dissect on the right side, it may be more difficult with a regular endoscope, which has its working channel on the left side. Thus, if the device can be pass to the right side, the procedure will be easier and faster.
2.1.2 Electrosurgical Unit
Development of endoscopic treatment with high-frequency electric surgical equipment is inseparable. Modern high-frequency electric surgical equipment has variety function. Fully understanding of the selection and settings of the mode is extremely important for the endoscopist.
ERBE electronic medical equipment are used commonly and it’s ENDO CUT (cutting and coagulation) and APC (argon plasma coagulation) modes are widely used worldwide. Now, ERBE has introduced the revolutionary Hybrid Knife system consists of the VIO electrosurgical unit, which acts as the master module, as well as an APC unit, ERBEJET 2 waterjet and EIP2 (Fig. 2.4).


Fig. 2.4
Hybrid Knife system (ERBE, Germany) consists of the VIO electrosurgical unit, which acts as the master module, as well as an APC unit, ERBEJET 2 waterjet and EIP2
2.1.2.1 Principle of Cutting and Coagulation
High-frequency alternating current can be used to rapidly heat the target tissue to temperatures above 100 °C. Rapid heating of tissue massively increases the vapor pressure, leading to the explosive rupturing of the cell membrane, which causes tissue cutting effect.
If tissue is heated (sufficiently slowly) using high-frequency alternating current up to a temperature of approx. 100 °C, the intra- and extra-cellular liquid vaporizes. Shrinking of cells due to desiccation causes compression of the tissue and glue-effect result in hemostasis(Fig. 2.5).
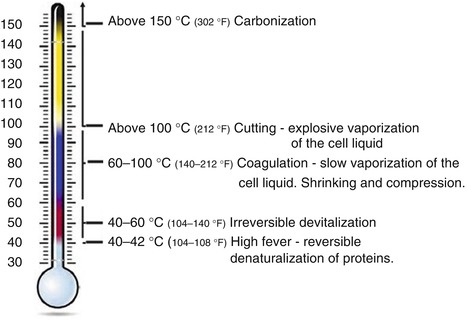

Fig. 2.5
Principle of cutting and coagulation
2.1.2.2 Monopolar and Bipolar Technology
Monopolar technology is defined that the current reaches neutral electrode through the human body and then back to a high-frequency generator.
Bipolar technology is defined that the current goes between the two poles (Fig. 2.6).
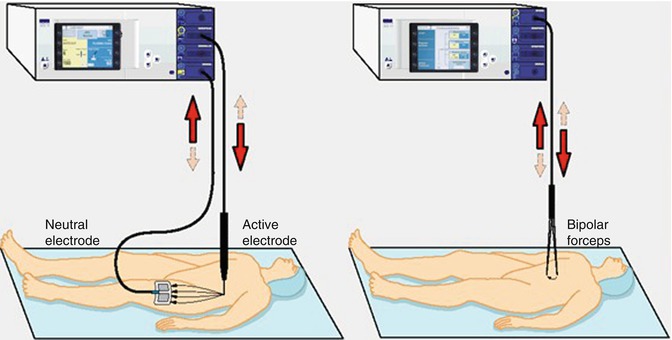

Fig. 2.6
Monopolar and Bipolar technology
2.1.2.3 Power Peak System (PPS)
The power output is dynamically regulated within the pre-set limits. It is independent of the cutting electrode, the velocity of the cutting and the tissue type (Fig. 2.7).
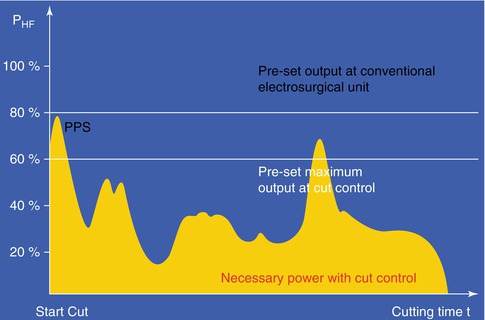

Fig. 2.7
Power Peak System
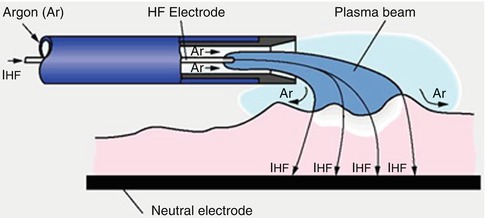
2.1.2.4 Principle of APC
Argon-plasma is electrically conductive like a wire. The current flows from the APC electrode to the tissue via the plasma. The electrode does not need to be in contact with the tissue.
Advantages of APC:
The coagulated tissue does not stick to the electrode.
Fast and expanded coagulation of superficial bleedings.
Controllable depth and lower risk of perforation (Fig. 2.9).

Fig. 2.9
APC has the advantage of controllable depth and lower risk of perforations
Less carbonization and less surgical smoke.
2.1.2.5 ENDO CUT IQ
The alternating cutting and coagulation cycles that characterize ENDO CUT can be varied, depending on size, shape and localization of the lesion in question-in terms of levels of effect, cutting duration and cutting interval (Figs. 2.10 and 2.11).
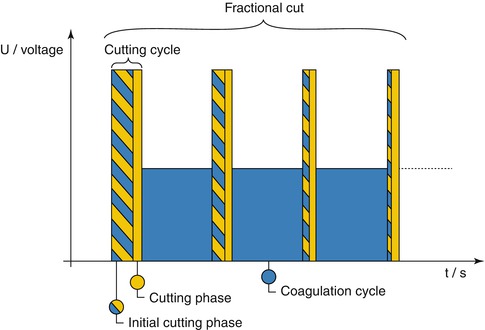

Fig. 2.10
ENDO CUT IQ

Fig. 2.11
ENDO CUT I is employed in ERCP; ENDO CUT Q is employed to EMR, ESD, POEM and STER
2.1.3 Flusher Equipment
2.1.3.1 Water Supply Equipment
Water supply equipment is a motorized pump designed to transfer water from a bottle, via a tube, to an endoscope. Olympus supplies UWS-1(Fig. 2.12) as a flushing pump, which includes two water tubes and instrument channel adapter to pump sterile water through the instrument channel of endoscope that is controlled by a footswitch.


Fig. 2.12
Olympus UWS-1
2.1.3.2 ERBE Jet2
ERBE Jet2 is a high pressure pump system (Fig. 2.13). ERBE Hybridknife uses ERBE Jet2 to create submucosal injection, cutting and dissection (Fig. 2.14). The Hybrid Knife delivers non-thermal jet that separates softer tissue from fibrin-rich layers and structures, thus minimizing the risk of accidental vessel injury and avoiding thermal tissue damage to deeper tissue layers.

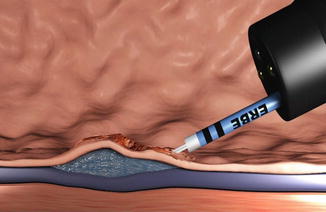

Fig. 2.13
ERBE Jet2

Fig. 2.14
ERBE JET2 for submucosa l injection
2.1.4 Carbon Dioxide Insufflation
Carbon dioxide can be absorbed rapidly by human tissue. Insufflation with carbon dioxide (instead of air) is popular in endoscopy procedures. It allows minimal sedation and reduces post procedural pain and possibly reduce the complications, such as compartment syndrome if perforations occur during ESD. It is recommanded that carbon dioxide insufflation for upper gastrointestinal ESD cases is better and safer than air insufflation (Fig. 2.15).