Chapter 5 Autoimmune hepatitis
Definition
TABLE 5.1 Autoimmune hepatitis: Basic diagnostic tests
| Diagnostic tests | Clinical value |
|---|---|
| Serum AST and ALT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and γ-globulin levels | Estimate severity of inflammatory activity; characterize pattern of liver injury |
| Serum albumin level and INR | Estimate impairment of hepatic synthetic function |
| ANA, SMA, anti-LKM1, and AMA | Document presence and nature of immune activity |
| Serum immunoglobulin levels | Confirm mainly serum IgG elevation |
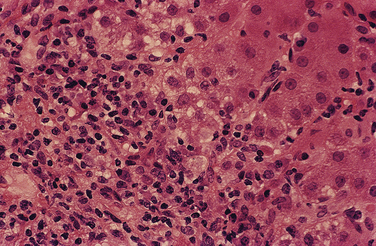
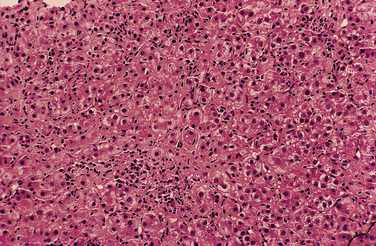
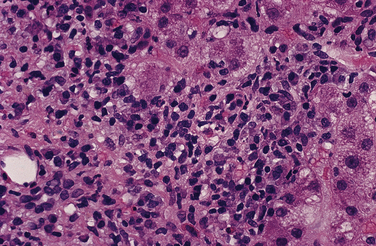
| Liver tissue examination | Document that histologic changes support diagnosis Exclude findings suggestive of other diagnoses |
| HBsAg, anti-HBc, IgM anti-HAV, and anti-HCV | Document absence of concurrent viral infection |
| Ceruloplasmin level | Exclude Wilson disease |
| Alpha-1 antitrypsin phenotype | Exclude alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency |
| Serum iron, transferrin, iron saturation and ferritin levels | Exclude hereditary hemochromatosis |
AMA, antimitochondrial antibodies; ANA, antinuclear antibodies; anti-HAV, antibody to hepatitis A virus; anti-HBc, antibody to hepatitis B core antigen; anti-HCV, antibody to hepatitis C virus; anti-LKM1, antibodies to liver kidney microsome type 1; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; IgG, immunoglobulin G; INR, international normalized ratio; SMA, smooth muscle antibodies.
Nomenclature
Diagnosis
TABLE 5.2 International criteria for definite or probable diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis
| Diagnostic features | Definite diagnosis | Probable diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Exclusion of risk factors for other diseases | ||
| Inflammatory indices | ||
| Autoantibodies | ANA, SMA, or anti-LKM1 >1:80 in adults and >1:20 in children; no AMA | ANA, SMA or anti-LKM1>1:40 in adults; other autoantibodies |
| Immunoglobulins | Globulin, γ-globulin, or IgG level >1.5 times normal | Hypergammaglobulinemia of any degree |
| Histologic findings |
AMA, antimitochondrial antibodies; ANA, antinuclear antibodies; AT, antitrypsin; anti-LKM1, antibodies to liver kidney microsome type 1; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; IgG, immunoglobulin G; SMA, smooth muscle antibodies.
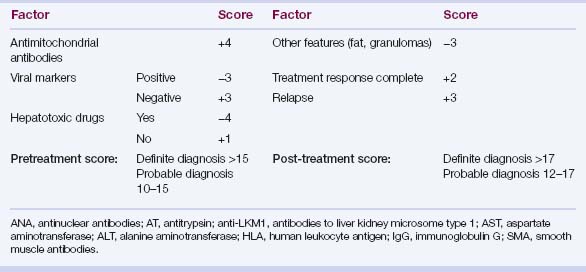
TABLE 5.4 Simplified international scoring system for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis
| Variable | Result | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Autoantibodies | ||
| ANA or SMA | ≥1:40 | +1 |
| ANA or SMA | ≥1:80 | +2 |
| anti-LKM1 | ≥1:40 | +2 |
| anti-SLA | Positive | +2 |
| Immunoglobulin level | ||
| Immunoglobulin G | >ULN | +1 |
| >1.1 ULN | +2 | |
| Histologic findings | ||
| Morphologic features | Compatible | +1 |
| Typical | +2 | |
| Viral disease markers | ||
| No viral hepatitis | No viral markers | +2 |
| Pretreatment aggregate score: | ||
| Definite diagnosis | ≥7 | |
| Probable diagnosis | 6 | |
ANA, antinuclear antibodies; anti-LKM1, antibodies to liver kidney microsome type 1; anti-SLA, antibodies to soluble liver antigen; SMA, smooth muscle antibodies; ULN, upper limit of normal.
Pathogenesis
Principal hypotheses
 A triggering viral, drug, toxic, or environmental agent that resembles a self-antigen (molecular mimicry)
A triggering viral, drug, toxic, or environmental agent that resembles a self-antigen (molecular mimicry) Presentation of antigenic peptide by the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DR molecule encoded by susceptibility alleles (DRB1∗0301 and/or DRB1∗0401 in white North Americans and northern Europeans)
Presentation of antigenic peptide by the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DR molecule encoded by susceptibility alleles (DRB1∗0301 and/or DRB1∗0401 in white North Americans and northern Europeans) A six amino acid motif within an antigen binding groove, encoded as LLEQKR (leucine-leucine-glutamic acid-glutamine-lysine-arginine) in positions 67 to 72 of the DRβ polypeptide chain, that optimizes autoantigen display in white North American and northern European patients
A six amino acid motif within an antigen binding groove, encoded as LLEQKR (leucine-leucine-glutamic acid-glutamine-lysine-arginine) in positions 67 to 72 of the DRβ polypeptide chain, that optimizes autoantigen display in white North American and northern European patients Lysine at position DRβ71 that facilitates contact among the HLA DR molecule, antigenic peptide, and T-cell antigen receptor of CD4 cell and that promotes susceptibility
Lysine at position DRβ71 that facilitates contact among the HLA DR molecule, antigenic peptide, and T-cell antigen receptor of CD4 cell and that promotes susceptibility Other autoimmune promoter genes in synergy (epistasis) with principal susceptibility alleles, including polymorphisms for cytotoxic T- lymphocyte antigen 4, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and Fas (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily-6) genes
Other autoimmune promoter genes in synergy (epistasis) with principal susceptibility alleles, including polymorphisms for cytotoxic T- lymphocyte antigen 4, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and Fas (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily-6) genes Activation of CD4 lymphocytes within the type 1 cytokine milieu (interleukin-12 [IL-12], IL-2, tumor necrosis factor alpha) and clonal proliferation of autoantigen-sensitized cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Activation of CD4 lymphocytes within the type 1 cytokine milieu (interleukin-12 [IL-12], IL-2, tumor necrosis factor alpha) and clonal proliferation of autoantigen-sensitized cytotoxic T lymphocytes Deficiencies in number and function of T-regulatory cells (CD4+CD25+ cells), which impair suppression of CD8+ T-cell proliferation and facilitate liver injury
Deficiencies in number and function of T-regulatory cells (CD4+CD25+ cells), which impair suppression of CD8+ T-cell proliferation and facilitate liver injury A triggering viral, drug, toxic, or environmental agent that resembles a self-antigen (molecular mimicry)
A triggering viral, drug, toxic, or environmental agent that resembles a self-antigen (molecular mimicry) A defect in suppressor activity or dysregulated cytokine homeostasis (e.g., increased constitutive or inducible amount or function of IL-10) favoring B-cell production of immunoglobulin G (IgG)
A defect in suppressor activity or dysregulated cytokine homeostasis (e.g., increased constitutive or inducible amount or function of IL-10) favoring B-cell production of immunoglobulin G (IgG) Antigen–antibody complexes on the hepatocyte surface targeted by natural killer cells with Fc receptors
Antigen–antibody complexes on the hepatocyte surface targeted by natural killer cells with Fc receptorsAncillary hypotheses
 Different susceptibility alleles encode the same or similar six amino acid motif within the antigen binding groove of the HLA DR molecule between positions 67 and 72 of the DRβ polypeptide chain and thereby affect susceptibility similarly.
Different susceptibility alleles encode the same or similar six amino acid motif within the antigen binding groove of the HLA DR molecule between positions 67 and 72 of the DRβ polypeptide chain and thereby affect susceptibility similarly. DRB1∗0301 and DRB1∗0401 (white North American and northern European patients), DRB1∗0404 (Mexican Mestizo patients), and DRB1∗0405 (Japanese, mainland Chinese, and adult Argentine patients) encode either LLEQKR or LLEQRR at positions DRβ67 to 72.
DRB1∗0301 and DRB1∗0401 (white North American and northern European patients), DRB1∗0404 (Mexican Mestizo patients), and DRB1∗0405 (Japanese, mainland Chinese, and adult Argentine patients) encode either LLEQKR or LLEQRR at positions DRβ67 to 72. Polymorphisms of genes inside and outside the major histocompatibility complex act in synergy with each other or the principal susceptibility alleles in a non–disease-specific fashion to promote susceptibility (“permissive gene pool”).
Polymorphisms of genes inside and outside the major histocompatibility complex act in synergy with each other or the principal susceptibility alleles in a non–disease-specific fashion to promote susceptibility (“permissive gene pool”). Polymorphisms of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene (TNFA-308), cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene (CTLA4∗G), and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily-6 gene (TNFRSF6∗G,G or ∗A,G) affect disease occurrence in white North American and northern European patients.
Polymorphisms of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene (TNFA-308), cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene (CTLA4∗G), and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily-6 gene (TNFRSF6∗G,G or ∗A,G) affect disease occurrence in white North American and northern European patients. Region- or ethnicity-specific susceptibility genes favor infection with or reactivity to indigenous etiologic agents, and the susceptibility allele is a “footprint” of the triggering agent.
Region- or ethnicity-specific susceptibility genes favor infection with or reactivity to indigenous etiologic agents, and the susceptibility allele is a “footprint” of the triggering agent. DRB∗1301 is the susceptibility allele for autoimmune hepatitis in Argentina and Brazil, especially among children, and it encodes a six amino acid sequence at positions DRβ67 to 72 (ILEDER) in which the substitution of glutamic acid (E) for lysine at DRβ71 defeats the shared motif hypothesis.
DRB∗1301 is the susceptibility allele for autoimmune hepatitis in Argentina and Brazil, especially among children, and it encodes a six amino acid sequence at positions DRβ67 to 72 (ILEDER) in which the substitution of glutamic acid (E) for lysine at DRβ71 defeats the shared motif hypothesis. DRB∗1301 is associated with protracted hepatitis A virus, and prolonged exposure to this viral antigen may predispose to autoimmune hepatitis in this geographic region.
DRB∗1301 is associated with protracted hepatitis A virus, and prolonged exposure to this viral antigen may predispose to autoimmune hepatitis in this geographic region.Subclassifications
Types
 Commonly associated with concurrent immune diseases, including vitiligo, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and autoimmune thyroiditis
Commonly associated with concurrent immune diseases, including vitiligo, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and autoimmune thyroiditis Frequent organ-specific autoantibodies (antibodies to parietal cells, thyroid, or islets of Langerhans)
Frequent organ-specific autoantibodies (antibodies to parietal cells, thyroid, or islets of Langerhans) Five antigenic sites located within recombinant CYP2D6; amino acid sequence between positions 193 and 212 main epitope of anti-LKM1
Five antigenic sites located within recombinant CYP2D6; amino acid sequence between positions 193 and 212 main epitope of anti-LKM1 Homologies between recombinant CYP2D6 and genome of hepatitis C virus, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus type 1
Homologies between recombinant CYP2D6 and genome of hepatitis C virus, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus type 1Variants
 Defined by features of autoimmune hepatitis, antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA), and histologic findings of bile duct injury or loss
Defined by features of autoimmune hepatitis, antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA), and histologic findings of bile duct injury or loss Most (88%) patients with AMA titers up to 1:160; seropositivity for antibodies to M2 autoantigens rare (8%) (see Chapter 14)
Most (88%) patients with AMA titers up to 1:160; seropositivity for antibodies to M2 autoantigens rare (8%) (see Chapter 14) Empiric treatment (3 to 6 months) with prednisone alone (20 mg daily) or prednisone (10 mg daily) plus azathioprine (50 mg daily) effective if autoimmune features predominant and alkaline phosphatase level less than twice the upper limit of normal (ULN)
Empiric treatment (3 to 6 months) with prednisone alone (20 mg daily) or prednisone (10 mg daily) plus azathioprine (50 mg daily) effective if autoimmune features predominant and alkaline phosphatase level less than twice the upper limit of normal (ULN) Defined by features of autoimmune hepatitis, cholestatic biochemical changes, histologic evidence of cholestasis including bile duct injury or loss, and abnormal bile ducts by endoscopic retrograde cholangiography (ERC) or magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRC)
Defined by features of autoimmune hepatitis, cholestatic biochemical changes, histologic evidence of cholestasis including bile duct injury or loss, and abnormal bile ducts by endoscopic retrograde cholangiography (ERC) or magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRC) Histologic features of bile duct injury, portal edema, and/or ductopenia and normal cholangiogram compatible with small duct PSC
Histologic features of bile duct injury, portal edema, and/or ductopenia and normal cholangiogram compatible with small duct PSC Clues to diagnosis: inflammatory bowel disease, suboptimal response to corticosteroid therapy, and/or rising serum alkaline phosphatase level
Clues to diagnosis: inflammatory bowel disease, suboptimal response to corticosteroid therapy, and/or rising serum alkaline phosphatase level Empirical therapy with prednisone (20 mg daily) and ursodeoxycholic acid (13 to 15 mg/kg daily) justified
Empirical therapy with prednisone (20 mg daily) and ursodeoxycholic acid (13 to 15 mg/kg daily) justified Children with autoimmune hepatitis and abnormal cholangiograms in the absence of inflammatory bowel disease (“autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis”) typically respond to corticosteroid therapy but have shorter transplant-free survival than patients with normal bile ducts
Children with autoimmune hepatitis and abnormal cholangiograms in the absence of inflammatory bowel disease (“autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis”) typically respond to corticosteroid therapy but have shorter transplant-free survival than patients with normal bile ducts SMA and ANA titers typically low in chronic viral hepatitis (up to 1:80 in 89%, 1:160 or higher in 11%; 1:320 or higher rarely)
SMA and ANA titers typically low in chronic viral hepatitis (up to 1:80 in 89%, 1:160 or higher in 11%; 1:320 or higher rarely)Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree