See Information: Autoimmune hepatitis I and II
Type 2 AIH: Liver–kidney–microsomal (LKM) positive
IgG significantly raised
Complement C3 and C4 low
Histology: plasma cell infiltrate of the portal tract which spills into the surrounding parenchyma (interface hepatitis), varying degrees of parenchymal collapse and fibrosis
Ultrasound: gallbladder enlarged and the bile ducts may be dilated and irregular
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatogram (MRCP): beading of bile ducts
Histology: onion skin fibrosis around the bile duct
See Information: Wilson’s disease
Low caeruloplasmin
ANA and SMA occasionally positive
Mildly raised IgG
Haemolytic anaemia
Low alkaline phosphatase
DNA: ATP7B mutations
Urine: 24-hour urine copper followed by a 24-hour urine collection after penicillamine at 0 and 12 hours if raised is very indicative of Wilson’s disease
MRI changes in basal ganglia
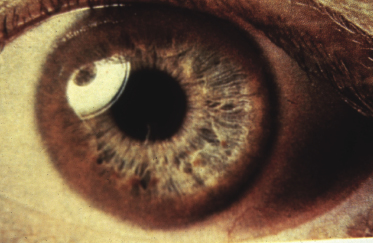
Ophthalmology: Kaiser–Fleisher rings Figure 21.1 Histology: micro and macro vesicular steatosis with varying degrees of portal inflammation and fibrosis; Mallory bodies, lipofuscin and copper will also be seen; liver for copper >250 μg/g dry weight (normal <55) is indicative
Histology: leukaemic infiltrate
Figure 21.1 Kaiser–Fleischer rings are usually only seen in Wilson’s disease after the age of 7 years.