CHAPTER 6 Voiding disorders and bladder outlet obstruction
INTRODUCTION
Causes of voiding difficulty in men are:
ANATOMICAL BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION
Benign prostatic obstruction
TERMINOLOGY: ENLARGEMENT OF THE PROSTATE
 Prostatectomy (usually trans-urethral prostatectomy [TURP]). Usage has declined in recent years due to the efficacy of medications in reducing symptoms and preventing progression. A variety of methods of performing prostatectomy or ablation of the prostate gland have been described including high intensity ultrasound, microwave thermotherapy, needle ablation, electro-vaporization and laser therapy. Open retropubic prostatectomy is also used in particularly large prostates where the open operation is quicker and safer than TURP. Prostatectomy is more successful in patients with demonstrable BOO on pressure/flow cystometry than in patients without documented obstruction
Prostatectomy (usually trans-urethral prostatectomy [TURP]). Usage has declined in recent years due to the efficacy of medications in reducing symptoms and preventing progression. A variety of methods of performing prostatectomy or ablation of the prostate gland have been described including high intensity ultrasound, microwave thermotherapy, needle ablation, electro-vaporization and laser therapy. Open retropubic prostatectomy is also used in particularly large prostates where the open operation is quicker and safer than TURP. Prostatectomy is more successful in patients with demonstrable BOO on pressure/flow cystometry than in patients without documented obstruction Trans-urethral incision of the prostate. Generally used for smaller prostates, the procedure has less associated morbidity than prostatectomy
Trans-urethral incision of the prostate. Generally used for smaller prostates, the procedure has less associated morbidity than prostatectomyCLINICAL NOTE: BENIGN PROSTATIC DISEASE
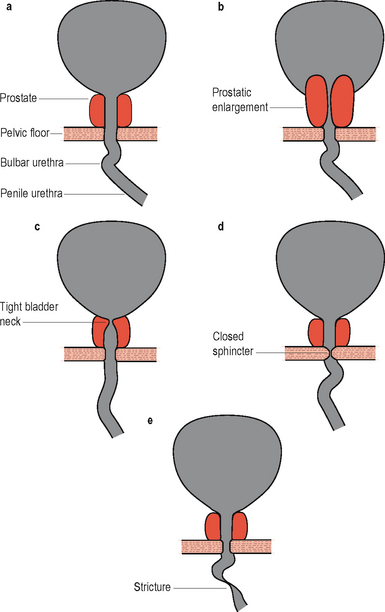
Bladder neck obstruction
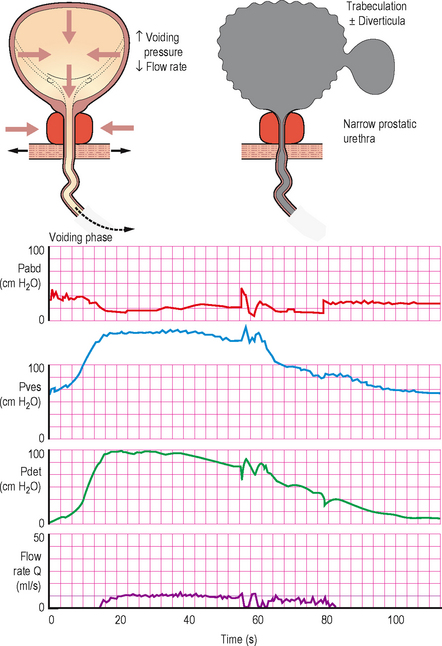
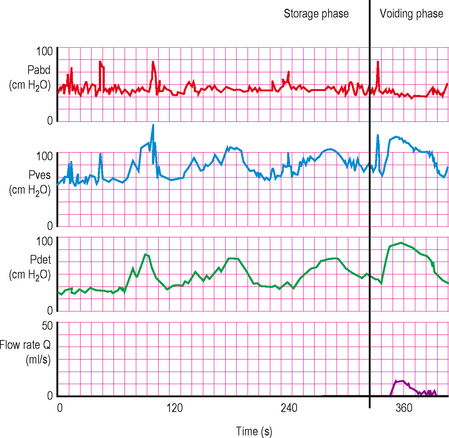
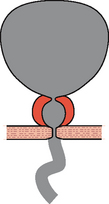
In this condition the bladder neck does not open completely during voiding and there is little or no flow during a well sustained detrusor contraction. Video urodynamics is necessary in order to make the diagnosis (Figure 6.1c). The condition is especially prevalent in younger men and also occurs occasionally in women; currently the aetiology of primary bladder neck obstruction is unknown. Theories for the cause include fibrosis, neurogenic dysfunction (detrusor/bladder neck dyssnergia) and smooth muscle hypertrophy, amongst others. On screening there may be trapping of contrast during the stop test (Figures 4.20 and 6.2).
Treatment of bladder neck obstruction includes:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree