Fig. 6.1
Small bowel anastomosis at CE: arrows indicate the presence of a double lumen, a finding consistent with a small bowel anastomosis provide that a diverticulum has been excluded
Another possible limitation of CE in this setting is related to the delayed capsule transit, which prevents, in operated patients, the complete evaluation of the small bowel. In the study by De Palma [10], where CE was performed in previously operated patients, the rate of complete evaluation of the small intestine was lower (about 70 %) than usually expected. The authors advocated the altered motility, resulting from the small bowel resection, as possible cause of the slow capsule transit.
Interestingly, in this study, all the ten enrolled patients excreted the capsule naturally; nevertheless, the surgically altered anatomy is a well-known risk factor for capsule retention, particularly in case of side-to-side anastomoses [11] in which the capsule can enter blind loops. In the study of De Palma [10], all patients were therefore screened, before undergoing CE by means of the small bowel follow-through to exclude critical stenosis. Subsequent studies have proposed to use, in patients with surgical anastomoses at risk for capsule retention, the patency capsule as “screening test” [12]. Although some studies [13] reported that the patency capsule can cause acute obstruction, the majority of available data [12, 14–16] especially in cases in which the Agile® patency capsule [17] was ingested, seem to suggest that this test is both safe, even in case of tight stenosis, and effective in selecting patients in whom CE could be performed safely.
6.2.2 Device-Assisted Enteroscopy
With the increased detection rate of small bowel lesions, by means of purely diagnostic procedures such as CE or radiological examinations, innovations in overtube-assisted deep enteroscopy have been crucial. Although some studies report that DAE is helpful in the diagnostic process (sometimes it is able to identify neoplastic lesions missed by other techniques) [18, 19], the main advantage of this procedure over CE is represented by its therapeutic and operative capabilities. DAE allows delivering therapies (i.e., hemostasis), but more importantly, in patients with small bowel anastomoses, to take biopsies, to place tattoos, and to perform balloon dilations.
In a recently published paper [20], the authors reported that all cases of small bowel neoplasm were histologically diagnosed on the of ground biopsies obtained during DAE and, interestingly, the tattoo placed during the procedure made the laparoscopic approach feasible in about 80 % of them.
Recent studies have also suggested a possible role for DAE in the endoscopic balloon dilation of small bowel strictures mostly in patients with Crohn’s disease or ischemic enteritis [21, 22]. In these patients, where the dilation was usually performed for disease-related stenosis, the technical success rate and the complication rate range between 80–100 % and 0–6 %, respectively [23]. Nevertheless, data about long-term outcome are lacking as well as those concerning results of postsurgical strictures dilation.
As far as limitations of DAE are concerned, this procedure is invasive, challenging, and time-consuming and requires trained endoscopists and, often, deep sedation or general anesthesia with intubation. Moreover, even when guided by other diagnostic procedures (i.e., CE or radiologic techniques), DAE can fail in reaching the small bowel finding. This often requires a new examination performed through the opposite route to access the small bowel [24]. The rate of entire small bowel examination, even when performed by DBE, which, although controversial results exist, seems to be the DAE with the highest small bowel completion rate [25, 26] is on average 40–50 % [23], with a wide range between the various published studies. Last but not least, although the complication rate of DAE appears to be low; severe complications (such as pancreatitis and bowel perforation) occur in about 1 % of all diagnostic procedures, whereas the complication rate of therapeutic procedures is reported to be higher, up to 4–5 % [27, 28]. Focusing the attention on operated patients, some authors reported an increased risk of perforation in patients with recently performed anastomosis [29]. On the other hand, the abdominal adhesions, which can arise after small bowel resection, can make DAE difficult to perform, less successful in exploring the small bowel, and more risky for the patients [27].
6.3 Endoscopic Surveillance of Small Bowel Anastomoses: Timing and Protocols
6.3.1 Preventing Postsurgical Complications
The most common complication of intestinal anastomosis is the development of ulcers [30]. Anastomotic ulcers may occur a few months to many years after surgery; in the study by Weinstock and Shatz [31], focused on ileocolonic anastomoses, the mean time frame between surgery and detection of ulcer was 5.1 years. Reaction to foreign body (Fig. 6.2) has been postulated as the main cause for the ulceration [32]; however, the majority of patients who have their anastomosis either with hand-sewn sutures or stapled do not develop ulcers. The local ischemia, secondary to scar formation, as well as abnormal motility and local intussusceptions, has also been advocated as mechanisms contributing to ulcer formation [30]. Although it has been postulated that some conditions (i.e., radiation therapy) can facilitate anastomotic ulceration, this complication appears to be unrelated to the clinical indication to small bowel resection and somewhat unpredictable. Therefore, although both CE (Fig. 6.3) and DAE are able to recognize the presence of small bowel anastomotic ulcers, the routine endoscopic surveillance of small bowel anastomoses, aimed at preventing this complication, is not recommended.
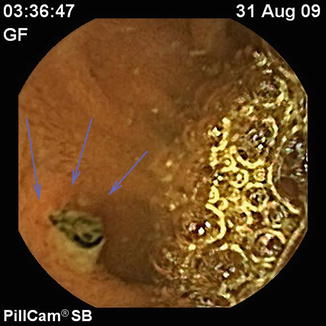
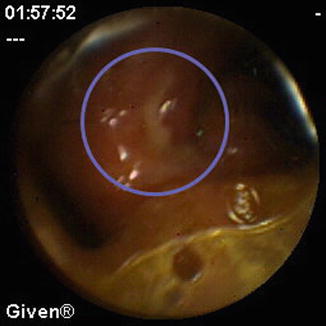

Fig. 6.2
Retained postsurgical suture at CE; arrows indicate the suture stitch

Fig. 6.3
Small bowel anastomotic ulcer at CE (inside the blue circle the ulcer covered by fibrin)
Conversely, at least from a theoretical point of view, there may be an indication to the endoscopic surveillance of small bowel anastomosis for those diseases with the potential for local recurrence, at the site of the anastomosis, such as Crohn’s disease or small bowel tumors.
6.3.2 Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease (CD) most commonly affects the ileocolonic region involving the small bowel up to 80 % of cases, while in about 30 % of patients, the disease is limited to the SB alone [33–35]. Therefore, in case of complication and/or failure of medical therapy, a significant proportion of patients with CD receive surgical interventions, and particularly ileocolonic resections, during their lifetime.
After ileal or ileocolonic resection, most patients have a postsurgical CD recurrence in the neoileum (endoscopic recurrence is indeed observed in almost 73 % of CD patients at 1 year and in 90 % at 3 years after curative resection) [36–38]. This recurrence follows a sequence of endoscopic lesions in the anastomotic and preanastomotic regions, followed by the development of clinical symptoms. The presence of extensive lesions in the neoileum area, identified through ileocolonoscopy in the months following surgery, predicts a rapid evolution to recurrent symptoms and eventual complications [39]. There are patient- and disease-related risk factors for postoperative recurrence: fistulizing disease, ileocolonic location, and a smoking habit increase the risk of recurrence [40–42]. Thus, these patients usually receive immunosuppressive therapy immediately after surgery. However, patients with a low risk of recurrence, such as nonsmokers and those with fibrostenotic disease, do not usually receive prophylactic treatment to prevent the development of new lesions. In such patients, clinical practice guidelines recommend that they undergo an ileocolonoscopy, grading the severity of lesions according to the Rutgeerts’ score, 6–12 months after resection [43, 44]. In this setting, the feasibility, the diagnostic performances, and the safety of CE have been explored.
Some studies reported CE diagnostic performances similar to that of ileocolonoscopy in recognizing lesions located at the site of anastomosis (sensitivity and specificity of CE 50–80 % and 94–100 %, respectively) [43, 45–47]. In addition, in these studies, CE was able to depict in a relevant proportion of patients, about 60 % [45, 47], inflammatory changes in the small bowel proximal to the anastomosis, although the clinical relevance of such lesions remains to be determined. Nevertheless, in these studies, about 10 % of patients developed, over time, anastomotic strictures and they could not undergo CE because of being tested positive to a patency capsule test [46].
In patients with CD, as far as the small intestine resections are concerned, strictureplasty is often performed. This way to restore the intestinal continuity allows avoiding extensive resections and consequently the risk of short bowel, but on the other hand, it creates large dilated loops with altered motility, potentially causing capsule retention [48].
Therefore, trying to translate the data collected with CE on the evaluation of ileocolonic anastomoses to small bowel anastomoses, and taking into account possible risks (capsule retention) and the low recurrence rate (lower than that observed in ileocolonic anastomoses) [49], it seems that a surveillance program, with CE, for evaluating the small bowel anastomoses in patients with CD cannot be proposed at the present time.
In this setting one should ask whether it is worthwhile to perform DAE for evaluating the small bowel. Theoretically, in these patients, the DAE could provide the same information of CE without the risk of capsule retention (Fig. 6.4). On the other hand, we have to take into account that DAE may be difficult to perform in patients with previously abdominal operations and an increased risk of perforation has been reported in case of severe inflammation of the small bowel wall and recently performed anastomoses [27].
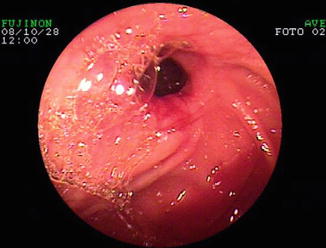

Fig. 6.4
Small bowel anastomotic stricture at DAE in a patient with Crohn’s disease
Unfortunately, to the best of our knowledge, there are no studies that have specifically addressed this type of assessment and this may represent an area for future research [50].
Endoscopic balloon dilation of small bowel strictures by DAE has the potential to obviate surgery in carefully selected patients [35, 51]. One study [52] showed that, an anastomotic stricture is an independent marker of the symptom-free outcome after enteroscopic balloon dilations. This emphasizes that, even with the limitations above mentioned, DAE has the potential to improve outcome of patients who previously underwent small bowel surgery.
6.3.3 Small Bowel Tumors
Small bowel tumors are a small proportion of gastrointestinal neoplasms; accounting for 1–3 % of all primary gastrointestinal tumors [53]. Nevertheless, recent studies suggest that the incidence of these diseases is increasing [53, 54]. Among malignant tumors, about 30–50 % are adenocarcinomas, 25–30 % are carcinoids, and 15–20 % are lymphomas [54]. As long as for some subtypes of small bowel lymphomas (i.e., follicular lymphoma) at the early stage, chemotherapy has been proposed as the primary curative therapy [55, 56], in the majority of cases, the surgical intervention, with en bloc resection, remains the cornerstone for the treatment of small bowel neoplams. Bilimoria et al. [54], collecting over the last 20 years more than 67,800 patients diagnosed with small bowel neoplasm, reported that about 80 % of them received surgical intervention. These data have also been confirmed by a recently published study [57] in which, in 141 patients with small bowel neoplasms, a segmental bowel resection was the most commonly used surgical procedure (about 70 % of cases).
After surgical resection, despite the differences between the various neoplasms, the restaging is usually carried out with imaging modalities (e.g., CT scan and/or FDG PET for lymphoma). There are no data, however, at present about the systematic use of CE or DAE in the follow-up of these patients.
The main limitation of CE in this specific setting, as reported above, is its low specificity (difficulty in distinguishing between surgical outcomes, postsurgical complications, or possible local recurrence of primary disease). This limitation could be easily overcome by DAE, which has also shown, at the time of the diagnosis, a diagnostic yield that, in some cases (i.e., lymphomas) (Figs. 6.5 and 6.6), was higher than that of other diagnostic methods (i.e., radiological) commonly used in the process of staging and restaging [58, 59].
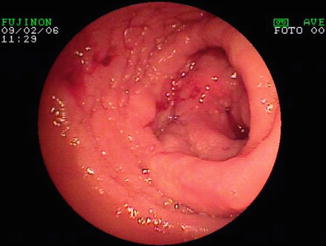
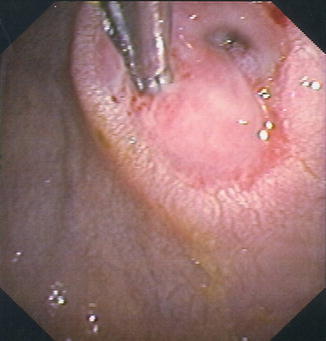

Fig. 6.5
Anastomotic recurrence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma identified at DAE

Fig. 6.6
Biopsy by DAE on a small bowel anastomotic stricture in a patient with recurrence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
6.4 Conclusions
So far, CE and DAE have been mainly used, in patients with small bowel resections, when complications or recurrence of the primary disease were suspected and imaging techniques resulted negative. Robust evidence about the possible role of these techniques as surveillance tools is lacking at the present time.
On the one hand, CE seems to be an ideal tool for a surveillance program (noninvasive, easy to perform, with high diagnostic yield), while on the other hand, it has some limitations (low specificity, risk of retention), hampering its application in this subset of patients. DAE could overcome CE limitations, allowing to perform biopsies, to place tattoos, and to dilate strictures; nevertheless, it is invasive, challenging, and burdened by possible serious complications.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








