Renal Function
Angela Cottrell
The kidney has a number of functions, including:
Maintenance of homeostasis.
Production of erythropoietin.
Maintenance of blood pressure.
Hydroxylation of vitamin D.
It is the investigation of the first of these with which this chapter is concerned.
Creatinine as an indicator of renal function
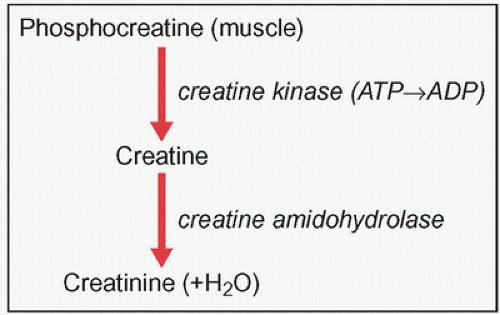
One of the major roles of the kidney is the excretion of soluble waste. This is achieved by the process of glomerular filtration. Creatinine is commonly used as an indicator of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Creatinine is a non-toxic breakdown product of creatine, a short-term energy store found in muscle (in the form of phosphocreatine) (1.1).
Laboratory analysis of serum creatinine entails chromographic analysis of the products of the Jaffe reaction. Creatinine is mixed with alkaline picramate and an orange coloured compound is formed (1.2). The product is then analysed by a colorimeter.
Table 1.1 shows possible causes for a raised creatinine.
The ‘goulash effect’ is a transient rise in serum creatinine after ingestion of large quantities of boiled meat.
Table 1.1 Causes of a raised creatinine | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Glomerular filtration rate
Measurement of serum creatinine has its limitations. The relationship between serum creatinine and GFR is not linear, and serum creatinine level may not rise significantly until GFR is as low as 30% of normal.
Clearance concept
GFR can be estimated by measuring clearances of a substance in which filtration by the glomerulus equals excretion in the urine. Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance by the kidneys per unit time (1.3).
Calculation of creatinine clearance (1.4)
Creatinine is an endogenous substance that is present at a relatively constant level. Measurements and calculation according to the formula in figure 1.3 require 24-hour collection of urine (1.5). Therefore, patients need to be compliant for results to be accurate.
Formulae to estimate GFR
Isolated measurements of serum creatinine are not accurate indicators of early renal disease. By incorporating variables such as age and weight, an estimated GFR can be derived.
Two commonly used formulae are those attributed to Cockcroft and Gault (1.6), and the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula (1.7).
The Cockcroft and Gault formula includes age, weight and sex to estimate creatinine clearance:
The four-variable MDRD formula is used in the UK Chronic Kidney Disease guidelines to calculate estimated GFR (eGFR).
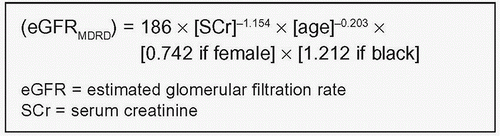 1.7 Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula. |
This estimate allows clinicians to classify the degree of renal impairment and hence determine further management (see Table 1.2).
Creatinine clearance measurement has its limitations. A small amount of creatinine is secreted by the renal tubules, and therefore GFR is likely to be overestimated if it is measured by this technique.
Table 1.2 Classification of chronic kidney disease | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||
Constant infusion technique
The gold standard method of measuring GFR is with inulin infusion. Inulin is a polymer of fructose that is derived from the tubers of dahlias. It is freely filtered by the glomerulus and neither secreted nor reabsorbed at the tubules. Accurate urine samples are taken following the infusion of inulin to maintain a constant concentration. This technique, although accurate, is limited to the research laboratory.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree