CHAPTER 2 Radionuclide Studies
![]() What are the half-lives of 99mTc, 123I, and 131I?
What are the half-lives of 99mTc, 123I, and 131I?
The half-lives are 6 hours, 13.2 hours, and 8 days, respectively.
![]() What exactly is a rad?
What exactly is a rad?
The amount of radiation energy absorbed by a patient’s tissue is expressed in rad. The rad is defined as 100 erg absorbed per gram of tissue.
![]() What is the difference between a roentgen and rad?
What is the difference between a roentgen and rad?
A roentgen is a measure of ionization of the air by x-rays or gamma rays. Although the terms roentgen and rad are often used interchangeably, it should be remembered that roentgen is a measure of exposure, whereas the rad is a measure of energy absorbed by tissue.
![]() What are the most common instruments used to clinically detect ionizing radiation?
What are the most common instruments used to clinically detect ionizing radiation?
Although gas detectors such as Geiger–Müller counters are used in nuclear medicine laboratories, solid crystal detectors are most commonly employed to detect ionizing radiation. The Anger camera used in most departments uses a sodium iodide crystal.
![]() What isotopes are used to measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
What isotopes are used to measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
Although 14C-inulin would give an accurate measurement of GFR, it is impractical to use. 51Cr-EDTA and 99mTc-DTPA are alternatives. In practice, 99mTc-DTPA is usually used, as it also provides excellent renal images.
![]() Which isotopes are useful in measuring renal blood flow (RBF)?
Which isotopes are useful in measuring renal blood flow (RBF)?
131I-hippuran, 123I-hippuran, and 99mTc-MAG3 are useful. 99mTc-MAG3 is most commonly used in the United States for these purposes.
![]() How is 99mTc-DTPA processed in the kidney?
How is 99mTc-DTPA processed in the kidney?
99mTc-DTPA is filtered and concentrated in the tubules and is then excreted through the collecting system. In a normal kidney, activity in the renal pelvis and ureter decreases after 5 to 10 minutes making it a useful test to detect obstruction.
![]() What does a DMSA scan demonstrate?
What does a DMSA scan demonstrate?
99mTc-DMSA accumulates progressively in the kidneys over several hours and images the renal cortex well. It is useful to detect renal scarring and early stages of renal damage from infection, and to differentiate functioning from nonfunctioning renal masses.
![]() What are the common uses of radionuclide studies after renal transplantation?
What are the common uses of radionuclide studies after renal transplantation?
They are useful in evaluating complications such as complete renal artery occlusion, urinary obstruction, or leakage. Acute tubular necrosis and rejection cause reduced perfusion and prolonged parenchymal transit times.
![]() What isotopes are useful in investigating occult suppuration in the abdomen or pelvis?
What isotopes are useful in investigating occult suppuration in the abdomen or pelvis?
Gallium-67 citrate–labeled or indium-111-labeled leukocytes are used.
![]() What is the advantage of scanning with indium-111-labeled leukocyte over gallium-67 citrate in localizing infection?
What is the advantage of scanning with indium-111-labeled leukocyte over gallium-67 citrate in localizing infection?
Studies with indium-111-labeled leukocytes often can be completed in 24 hours, whereas those using gallium-67 may take 48 to 72 hours to complete. In addition, the latter may be taken up by certain tumors such as lymphomas and hepatomas and is taken up by kidneys, which may confuse the diagnosis.
![]() How is mercaptoacetyltriglycine (MAG3) cleared by the kidneys?
How is mercaptoacetyltriglycine (MAG3) cleared by the kidneys?
MAG3 is cleared by the kidneys primarily by tubular secretion and to a lesser extent by glomerular filtration. Therefore, it is an excellent agent for estimating the effective renal plasma flow. It is used to define ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction and differential renal function.
![]() What is nuclear cystography and what is its value in ureteral reflux?
What is nuclear cystography and what is its value in ureteral reflux?
It is the scintigraphic equivalent of conventional cystography. It is an accurate method for detecting and following reflux, although it does not provide the anatomic detail of fluoroscopic studies.
![]() True/False: In screening siblings for reflux, the nuclear scan is preferable to a standard voiding cystography.
True/False: In screening siblings for reflux, the nuclear scan is preferable to a standard voiding cystography.
True. The radiation exposure in a nuclear scan is lower than that in a cystogram and when anatomic detail of VCUG is not essential, the nuclear scan is preferable.
![]() What are the nuclear scan findings in testicular torsion?
What are the nuclear scan findings in testicular torsion?
The testicle appears avascular. In cases of epididymitis hypervascularity is noted. However, in cases of intermittent torsion and late torsion, hypervascularity may result from an inflammatory response. Occasional false-positive and false-negative results and limited availability of the nuclear scan 24 hours a day limit its usefulness in the diagnosis of torsion.
![]() What is the “doughnut sign” on the nuclear scan in testicular torsion?
What is the “doughnut sign” on the nuclear scan in testicular torsion?
In a missed torsion (ie, one that is several days old), there is often an area of hyperemia surrounding the central ischemic region of the testis. The central area appears photopenic surrounded by a rim of increased activity (doughnut).
![]() What factors affect the drainage curve of the nuclear scan in patients with UPJ obstruction?
What factors affect the drainage curve of the nuclear scan in patients with UPJ obstruction?
In addition to the severity of obstruction, the size and compliance of the collecting system, and the hydration of the patient, the timing of diuretic and bladder drainage influences the drainage curve. A poorly functioning kidney may not respond adequately to the diuretic.
![]() True/False: The advantages of the 99mTc-DMSA scan over IVU in the evaluation of renal damage from pyelonephritis include (a) lack of study impairment by bowel gas, (b) earlier detection of renal damage, (c) clear visualization of kidneys despite overlying bony structures, (d) improved ability to image the kidneys in various positions to delineate specific lesions, and (e) more clear visualization of the collecting system.
True/False: The advantages of the 99mTc-DMSA scan over IVU in the evaluation of renal damage from pyelonephritis include (a) lack of study impairment by bowel gas, (b) earlier detection of renal damage, (c) clear visualization of kidneys despite overlying bony structures, (d) improved ability to image the kidneys in various positions to delineate specific lesions, and (e) more clear visualization of the collecting system.
False. All are true except that the visualization of the collecting system in the DMSA scan is not nearly as good as with an IVU.
![]() True/False: Captopril is used to improve the accuracy of nuclear scan findings of renovascular hypertension.
True/False: Captopril is used to improve the accuracy of nuclear scan findings of renovascular hypertension.
True. Captopril exaggerates the differences between the perfused and nonperfused areas of the kidney in patients with renovascular hypertension.
![]() What is the rationale behind the performance of a captopril renogram in the diagnosis of obstructive uropathy?
What is the rationale behind the performance of a captopril renogram in the diagnosis of obstructive uropathy?
Renin is secreted by the juxtaglomerular apparatus in renovascular hypertension and/or obstructive uropathy as a result of poor tissue perfusion. The local vascular regulatory mechanisms of the kidney are:
• Release of thromboxane, causing vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole, resulting in a further decrease of RBF
• Activation of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) that results in the formation of angiotensin II, which in turn increases the efferent arteriolar tone and is primarily responsible for restoring and maintaining glomerular filtration pressure
Use of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) such as captopril can block this mechanism by preventing the formation of angiotensin II that reduces the vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole, thereby causing a drop in GFR and relative renal function. This decrease is demonstrable with captopril renography.
![]() What is the correct dose of captopril administered for a captopril renogram?
What is the correct dose of captopril administered for a captopril renogram?
0.3 mg/kg is administered orally 1 hour prior to the radioisotope injection. A change of at least 5% (baseline scan vs captopril scan) is considered significant when interpreting the results.
![]() What is an MIBG scan and what is it used for?
What is an MIBG scan and what is it used for?
Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) is taken up by adrenal neurons. It is labeled with iodine and used to image the adrenal medulla and other active adrenergic tissues such as pheochromocytomas and neuroblastomas.
![]() How are nuclear scans helpful in carcinoma of the prostate?
How are nuclear scans helpful in carcinoma of the prostate?
Bone scans with 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate (MDP) are most useful in the staging of prostate cancer. They are more than 95% sensitive in detecting bony metastases from carcinoma of the prostate.
![]() What is a “superscan” in a patient with prostate cancer?
What is a “superscan” in a patient with prostate cancer?
When there is extensive involvement of the bony skeleton with metastases in a patient with prostate cancer, the isotope is extensively taken up by the bone and the kidneys are not visualized.
![]() Bone scans typically are almost always negative and therefore not particularly useful until the PSA level reaches what point?
Bone scans typically are almost always negative and therefore not particularly useful until the PSA level reaches what point?
A PSA level of 20 or more is usually necessary before a bone scan will be positive.
![]() Can nuclear scans be used in renal failure?
Can nuclear scans be used in renal failure?
Yes. 123I and 131I-hippurate and MAG3 can be concentrated even in kidneys with minimal renal function. They are of immense value in patients with renal failure or renal transplantation.
![]() What are the features of renal obstruction in a patient with hydronephrosis on a nuclear scan?
What are the features of renal obstruction in a patient with hydronephrosis on a nuclear scan?
During the excretory phase of the scan, the renogram demonstrates increasing activity over time, even after administration of furosemide, but the test may be unreliable in patients with poorly functioning kidneys or massively dilated collecting systems.
![]() How accurate is the MIBG scan in localizing pheochromocytomas and neuroblastomas?
How accurate is the MIBG scan in localizing pheochromocytomas and neuroblastomas?
123I-MIBG scan is 85% to 90% sensitive and nearly 100% specific for localizing pheochromocytomas. It is almost 100% specific and 100% sensitive for neuroblastomas.
![]() What constitutes a “well-tempered renogram” and how is it done?
What constitutes a “well-tempered renogram” and how is it done?
The Society for Fetal Urology and the Pediatric Nuclear Medicine Council of the Society of Nuclear Medicine published guidelines for the “well-tempered diuresis renogram” in 1992:
• Small field of view gamma camera is used for pediatric studies.
• If the child is younger than 4 months, MAG3 should be the radioisotope used for the study.
• In children older than 4 months, MAG3 is still the preferred radioisotope. However, DTPA may be substituted instead.
• The patient is well hydrated. A normal saline IV (15 mL/kg) bolus given over 30 minutes is begun 15 minutes prior to the administration of the radioisotope. For the remainder of the study, a maintenance IV at 200 mL/kg/24 h is administered. The child’s bladder should be catheterized to prevent any lower urinary tract dysfunction from influencing the results of the study.
![]() What is the recommended dose of diuretic (furosemide) for a “well-tempered diuresis renogram?”
What is the recommended dose of diuretic (furosemide) for a “well-tempered diuresis renogram?”
The dose of diuretic (Lasix) used should be 1 to 2 mg/kg IV.
![]() What is an indirect radionuclide cystogram (IRC)?
What is an indirect radionuclide cystogram (IRC)?
The IRC is a diagnostic test to detect vesicoureteral reflux (VUR). It employs 99mTc-DTPA as the radionuclide tracer. It provides information about the emptying phase of the bladder and can demonstrate VUR. Since it does not provide any information about the filling phase, it will miss the 3% of VUR known to occur during this phase of the bladder cycle. The high sensitivity of the IRC combined with the advantages of lower radiation and avoidance of bladder catheterization makes it a valuable alternative to the VCUG.
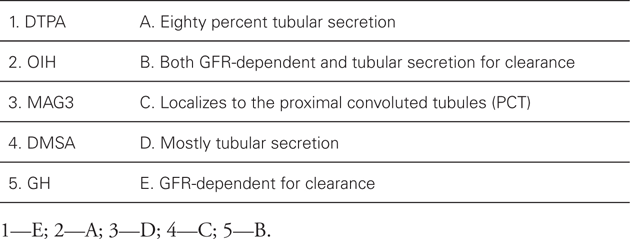
![]() Match the following radionuclide tracers with method of action tracers:
Match the following radionuclide tracers with method of action tracers:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


