Chapter 31 Liver transplantation
Overview
Selection of Candidates
Indications for liver transplantation
table 31.1 Indications for liver transplantation in adults
| Category | Disease |
|---|---|
| Noncholestatic or inflammatory | |
| Cholestatic | |
| Metabolic | |
| Malignant | |
| Extrahepatic | |
| Miscellaneous |
Assessment of liver disease severity
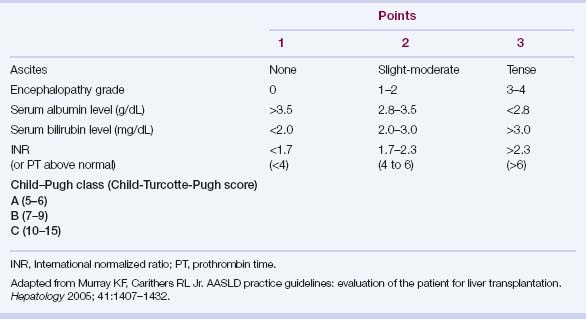
An accurate assessment of the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with progressive ESLD is critical to determining the appropriate timing for referral to a liver transplant center and is a key factor in prioritization for transplantation.
 This score was developed to predict operative mortality in persons with cirrhosis who required portacaval shunt surgery for variceal bleeding.
This score was developed to predict operative mortality in persons with cirrhosis who required portacaval shunt surgery for variceal bleeding. The MELD was initially developed to predict 3-month mortality in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement.
The MELD was initially developed to predict 3-month mortality in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement. The components—serum creatinine and total bilirubin levels and the international normalized ratio (INR) of prothrombin time—are key determinants of survival (Table 31.3).
The components—serum creatinine and total bilirubin levels and the international normalized ratio (INR) of prothrombin time—are key determinants of survival (Table 31.3).TABLE 31.3 Model for End-stage Liver Disease
| MELD score = 9.57 × loge (serum creatinine [mg/dL]) + 3.78 × loge (serum bilirubin [mg/dL]) + 11.20 × loge (INR) + 6.43 |
INR, international normalized ratio; MELD, Model for End-stage Liver Disease.
Adapted from Wiesner R, Edwards E, Freeman R, et al. Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) and allocation of donor livers. Gastroenterology 2003; 124:91–96.
TABLE 31.4 Clinical stages of cirrhosis and mortality risk
| Stage | Complications | 1-yr mortality risk (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 3.4 | |
| 3 | Ascites present | 20 |
| 4 | Variceal hemorrhage | 57 |
Adapted from D’Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol 2006; 44:217–231.
Referral to a liver transplant center
Liver transplant evaluation
In addition to hepatology and transplant surgery consultations, a liver transplant evaluation includes various laboratory tests, imaging studies, and other consultations (Table 31.5).
TABLE 31.5 Liver transplant evaluation
| Extensive laboratory testing for accurate assessment of current clinical status, evaluation of potential causes of underlying chronic liver disease, and screening for comorbid illnesses |
| Accurate assessment of renal function |
| Imaging for surveillance for HCC, assessment of hepatic vasculature, and evaluation of hepatic anatomy |
| Cardiopulmonary evaluation, which may include right or left heart catheterization, depending on risk factors |
| Psychosocial assessment |
| Age-appropriate screening tests including colonoscopy, mammogram, PSA level, and Pap test |
HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; PSA, prostate-specific antigen.
Contraindications to liver transplantation (Table 31.6)
TABLE 31.6 Contraindications to liver transplantation