Chapter 11 Laparoscopy-Assisted Distal Gastrectomy for Cancer
Operative indications
The indication of LADG for advanced cancer remains controversial because of the lack of clinical evidence of oncologic safety. Most surgeons who perform open surgery worry about the possibility of an increased incidence of port-site recurrence and peritoneal metastasis. Therefore, LADG in Japan is applied to AGC without serosal invasion and lymph node status of N2 or higher. The extent of LN dissection in Japan is determined according to the predicted frequency of LN metastasis. The Japanese Gastric Cancer Association guidelines indicate the following: D1 or D1+ for EGC, and D2 for AGC (see definitions in Fig. 11-1 and Tables 11-1 and 11-2).
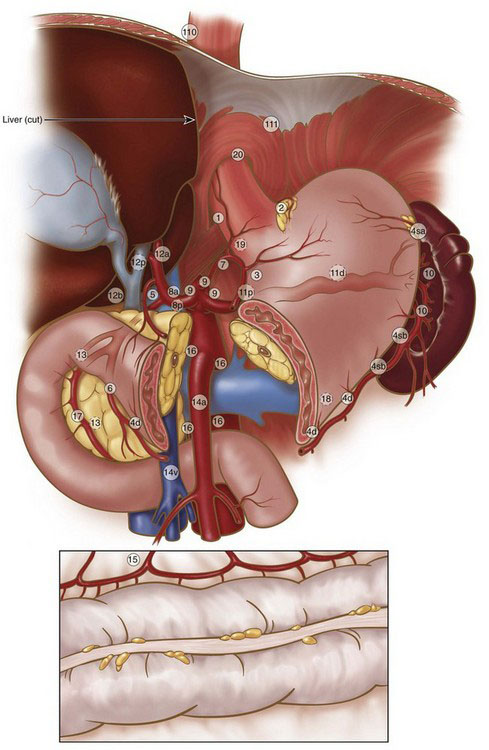
FIGURE 11-1 Regional lymph nodes.
(Adapted from Japanese Gastric Cancer Association: Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma, 2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer 1:10–24, 1998.)
Table 11-1 Lymph Node Stations of the Japanese Classification System for Gastric Cancer*
| No. | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Right paracardial LN |
| 2 | Left paracardial LN |
| 3 | LN along the lesser curvature |
| 4sa | LN along the short gastric vessels |
| 4sb | LN along the left gastroepiploic vessels |
| 4d | LN along the right gastroepiploic vessels |
| 5 | Suprapyloric LN |
| 6 | Infrapyloric LN |
| 7 | LN along the left gastric artery |
| 8a | LN along the common hepatic artery (anterosuperior group) |
| 8p | LN along the common hepatic artery (posterior group) |
| 9 | LN around the celiac artery |
| 10 | LN at the splenic hilum |
| 11p | LN along the proximal splenic artery |
| 11d | LN along the distal splenic artery |
| 12a | LN in the hepatoduodenal ligament (along the hepatic artery) |
| 12b | LN in the hepatoduodenal ligament (along the bile duct) |
| 12p | LN in the hepatoduodenal ligament (behind the portal vein) |
| 13 | LN on the posterior surface of the pancreatic head |
| 14v | LN along the superior mesenteric vein |
| 14a | LN along the superior mesenteric artery |
| 15 | LN along the middle colic vessels |
| 16a1 | LN in the aortic hiatus |
| 16a2 | LN around the abdominal aorta (from the upper margin of the celiac trunk to the lower margin of the left renal vein) |
| 16b1 | LN around the abdominal aorta (from the lower margin of the left renal vein to the upper margin of the inferior mesenteric artery) |
| 16b2 | LN around the abdominal aorta (from the upper margin of the inferior mesenteric artery to the aortic bifurcation) |
| 17 | LN on the anterior surface of the pancreatic head |
| 18 | LN along the inferior margin of the pancreas |
| 19 | Infradiaphragmatic LN |
| 20 | LN in the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm |
| 110 | Paraesophageal LN in the lower thorax |
| 111 | Supradiaphragmatic LN |
| 112 | Posterior mediastinal LN |
* See Fig. 11-1 for illustration of station positions.
Data from Japanese Gastric Cancer Association: Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma, 2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer 1:10–24, 1998.
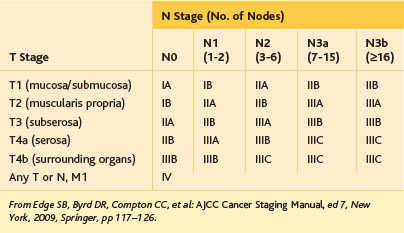
Table 11-2 Extent of Lymph Node Dissection (D Type) with Respect to Gastric Tumor Stage for Distal Gastrectomy*
| Type | Stations | Applicable Tumor Stage |
|---|---|---|
| D1 | 1, 3, 4sb, 4d, 5, 6, 7 | T1a tumor without indication for endoscopic resection; well-differentiated T1b tumor smaller than 1.5 cm with cN0 |
| D1+ | D1 stations, plus 8a, 9 | T1 tumor with cN0 (other than listed above) |
| D2 | D1 stations, plus 8a, 9, 11p, 12a | T1 tumor with cN(+); resectable T2 (or deeper) tumor |
* See Fig. 11-1 and Table 11-1 for definition of lymph node stations; see Table 11-3 for tumor staging.
Preoperative evaluation, testing, and preparation
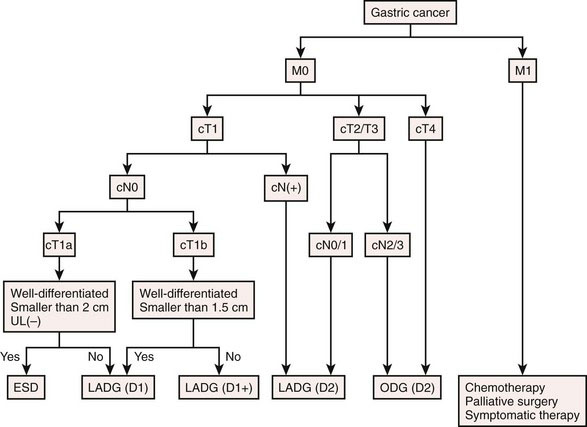
Preoperative evaluation should stage the gastric cancer and the patient’s systemic tolerance to surgical stress. Gastric tumor staging as defined by the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) is shown in Table 11-3. For the staging of gastric cancer, endoscopic examination (with biopsy and ultrasound) and barium meal study are used to evaluate the location, histologic type, size, and depth of wall invasion of the gastric cancer. Ultrasound examination and CT are used to evaluate invasion to other organs, nodal metastasis, hematogenous metastasis, and peritoneal dissemination. AGC without serosal exposure (T2) is diagnosed by laparoscopic examination under the same anesthetic as LADG. An algorithm of treatment selection for various subtypes of EGC and AGC is shown in Figure 11-2. To determine systemic tolerance to surgical stress, heart, respiratory, liver, and kidney function are evaluated in the same manner as with open surgery.