Chapter 6 Laparoscopic Esophageal Mucosal Resection for High-Grade Dysplasia
Positioning and placement of trocars
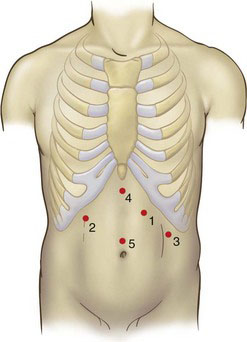
The patient is placed in a modified French lithotomy position with 30-degree reverse Trendelenburg (see Fig. 5-1 in Chapter 5). The surgeon stands between the patient’s legs, the camera operator stands to the patient’s right, and the first assistant stands to the patient’s left. Five trocars are placed as shown in Figure 6-1. The initial port (number 1) is placed using the optical trocar in the left midclavicular line subcostally and serves as the surgeon’s operating right hand. Subsequent trocars are placed in the order numbered two through five. The basic principles of trocar position and use should be followed: The camera port (number 5) is in the midline superior to the umbilicus. The surgeon’s left-hand working port (number 2) is placed in the right subcostal region in the midclavicular line. The retraction port for the assistant (number 3) is placed in the left midaxillary line caudad to port number 1. Trocar number 4 is used to retract the left lateral lobe of the liver and is placed in the subxiphoid region.
Operative technique
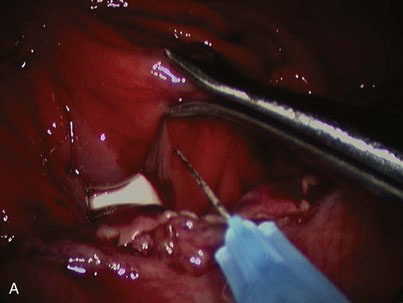
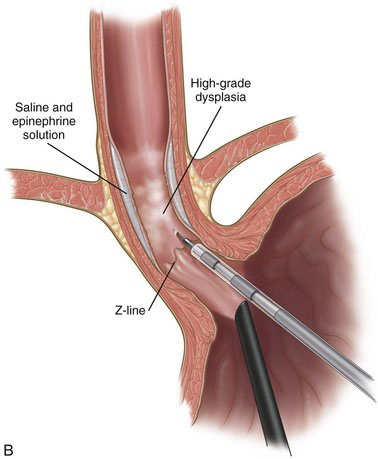
A solution of epinephrine and normal saline (1 : 100,000) is injected with a retractable hypodermic needle system at the Z-line of the distal esophagus to aid in the elevation of the mucosa (Fig. 6-2). The submucosal plane is entered with a modified hook electrocautery instrument; the hook is completely insulated except for the superior edge to allow contact with the underlying muscular layer and not cause thermal injury (Fig. 6-3). The mucosa is dissected further from the underlying smooth muscle with a curved laparoscopic spatula (Fig. 6-4). The mucosa is circumferentially dissected and excised in four quadrants. The mucosal segment is then excised using hook scissors. The tapered end of a lighted bougie (Medovations Inc., Milwaukee, Wis.) maneuvered by laparoscopic forceps is used as a retractor for exposing the four quadrants of mucosa (Fig. 6-5). The excised mucosa is oriented and marked for proximal and distal pathologic orientation. The raw surface of the esophagus is irrigated profusely, and any bleeding is controlled with cautious use of electrocautery. The esophageal wall in the area of mucosal resection is checked for intactness.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree