Fig. 23.1
CT scan showing multiple left paraaortic and interaortico-caval LNs consistent with EGGCT. Teratoma was seen in most of them (Courtesy of Dr J-L Hoepffner, Onco-Urologist, Saint-Augustin Clinic and Bergonié Oncological Institute, Bordeaux, France)
The metastatic pattern of EGCCT also depends on the site and the histological type [4]:
Mediastinum: Seminomas to cervical LN and nonseminoma to lungs (27 %).
Retroperitoneum: Seminomas to retroperitoneal LN (26 %) and then to mediastinal and cervical LN. Nonseminomas to the lungs (49 %), abdominal LN (34 %) and liver (25 %). Metastases to the brain and bone have also been reported.
23.1 Treatment of EGGCT
Retroperitoneal GCTs should be treated in a similar fashion as testicular tumours.
Seminomatous EGGCT: Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is the standard treatment and is credited for >90 % 5-year survival rate. Radiotherapy harbours a high rate of disease relapse; it carries a 5-year progression-free survival rate of 33 % compared with 87 % for chemotherapy [3]. Surgery is indicated if active residual masses are diagnosed, applying similar criteria as in testicular GCTs.
Nonseminomatous EGGCT: PEB chemotherapy has a median survival rate of 34 months. Surgery is indicated for residual masses or persistently high tumour markers (Fig. 23.2a, b).
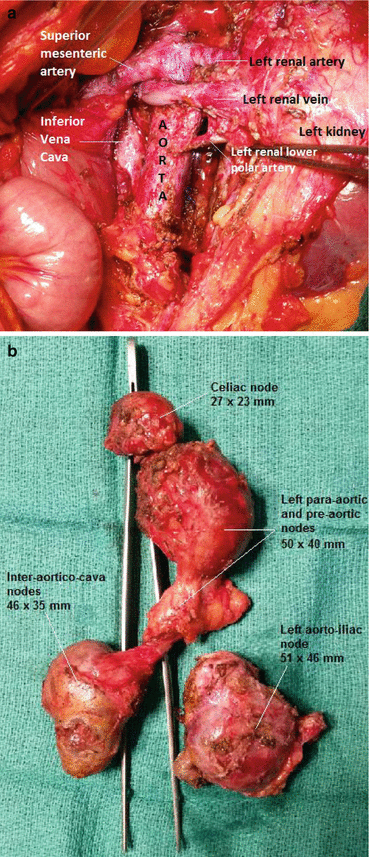
Fig. 23.2
(a, b) View of the retroperitoneum after an RPLND (same patient on Fig. 23.1) and the removed LNs (the forceps in Figure b reproduces the relative position of the aorta) (Courtesy of Dr J-L Hoepffner, Onco-Urologist, Saint-Augustin Clinic and Bergonié Oncological Institute, Bordeaux, France)
Mediastinal nonseminomatous EGGCTs have an overall 5-year survival rate of 45 and 17 % for intermediate- and poor-risk groups, respectively, defined as per the same IGCCCG criteria seen on Table 21.3 [4]. A study recently performed at Indiana University suggests replacing bleomycin by ifosfamide for patients with mediastinal nonseminomatous EGGCTs to prevent pulmonary complications, as these patients generally require extensive thoracic surgical resection [9].< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







