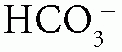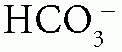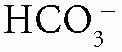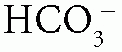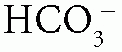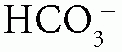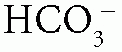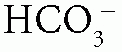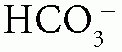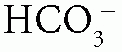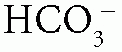Acid-Base Disorders
Andrei Brateanu
Craig Nielsen
RAPID BOARD REVIEW—KEY POINTS TO REMEMBER:
Steps in analyzing acid-base disorders:
Verify the internal consistency of the data:
Determine the arterial blood pH:
In the presence of a normal pH:
If pH < 7.35 patient has acidemia.
If pH > 7.45 patient has alkalemia.
Determine if the primary disorder is:
In metabolic acidosis:
if CO2 is higher, a respiratory acidosis is also present;
if CO2 is lower, a respiratory alkalosis is also present.
When the patient has normal AG (hyperchloremic) metabolic acidosis, calculate the urine anion gap (UAG) = urine Na+ + urine K+ – urine Cl–:
When the patient has high AG metabolic acidosis, calculate the osmolal gap = osmolalitymeasured – (2·[Na+] + glucose/18 + BUN/2.8) and measure toxins if poisoning suspected, or osmolal gap is high (N < 10 mOsm/L).
When the patient has a high AG metabolic acidosis calculate “Delta Delta”

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree